Topic: (Nysed) Cellular Respiration
(Nysed) Cellular Respiration
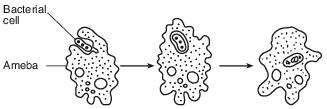
This process is essential to the survival of the ameba because it
(1) provides materials used in cellular respiration
(2) removes pathogens from the environment
(3) supplies the raw materials for photosynthesis
(4) protects the organism during development
In the cells of the human body, oxygen molecules are used directly in a process that
(1) releases energy
(2) digests fats
(3) synthesizes carbohydrate molecules
(4) alters the genetic traits of the cell
The energy released when sugar molecules are broken down is stored in
(1) minerals
(2) ATP
(3) DNA
(4) wastes
In the human body, carbon monoxide reduces the amount of oxygen that can be transported to cells. Breathing in too much carbon monoxide will most likely result in the production of
(1) less ATP
(2) less glucose
(3) more DNA
(4) more protein
The diagram below shows part of the human body with some organs that help to carry out the removal of wastes.

The energy necessary to perform this function comes directly from the
(1) exchange of H2O and O2 during respiration
(2) blood flowing through the organs
(3) ATP molecules produced during cellular respiration
(4) water that is eliminated by the organs

Molecules 1 and 2 are most likely
(1) carbon dioxide and oxygen
(2) carbon dioxide and water
(3) nitrogen and oxygen
(4) nitrogen and water
During cellular respiration, what is the direct source of the energy used in the cells of consumers in the ecosystem represented below?

(1) the Sun
(2) enzymes
(3) the atoms making up inorganic molecules
(4) the chemical bonds in organic molecules
Which dissolved substance do aquatic animals remove from their external environment for use in cellular respiration?
(1) carbon dioxide
(2) ATP molecules
(3) oxygen molecules
(4) nitrogen gas
It may be harmful when people compete to see who can hold their breath the longest under water. Without oxygen, brain cells
(1) cannot make enough ATP
(2) have too few mitochondria
(3) make too many enzymes
(4) have too much water
The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells.

Which molecule is indicated by X?
(1) glucose
(2) ATP
(3) carbon dioxide
(4) protein
Blood Doping
Blood is a fluid tissue, which means that blood cells are suspended in a fluid called plasma. Blood tests are concerned with not only the number of blood cells present, but with the amount of plasma that surrounds the cells.
The diagram below represents tubes containing blood samples from an athlete before and after blood doping. Blood doping is an illegal practice reportedly used by some athletes a few weeks before an athletic event, and involves removing whole blood from an athlete, separating the oxygen-carrying red blood cells (RBCs), and then freezing them. These RBCs are thawed and returned to the athlete’s body just before the athlete competes. Serious health risks are associated with this practice.

Explain why athletes who practice blood doping would be expected to perform better at an athletic event. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The practice increases the number of RBCs that would carry more oxygen to muscle cells.
• — Since muscle cells receive more oxygen for respiration, they would have more energy for
• the athletic event.
• — They would have more energy because they have extra oxygen.
A student measured oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration levels in an aquatic ecosystem during a 24 hour period. The data are represented in the graph below.
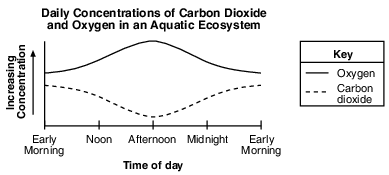
Identify two biological processes that are responsible for the production of varying amounts of carbon dioxide and oxygen within the aquatic ecosystem. [1]
Processes: ____________________________________ and ____________________________________
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — respiration and photosynthesis
• — photosynthesis and aerobic respiration
• — photolysis and respiration

Explain why most human cells require a supply of glucose. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Cells require a supply of glucose to produce ATP.
• — Cells need glucose to carry out cellular respiration.
• — Cells need glucose to release energy/for energy/as a source of energy.
• — Glucose is needed to provide energy for cells.
Process 1: oxygen + glucose → carbon dioxide + water + X
Process 2: carbon dioxide + water → oxygen + glucose
Identify the molecule represented by letter X in process 1. [1]
Allow 1 credit for ATP or adenosine triphosphate.

Identify one specific molecule used to store the energy being released during this process. [1]
Molecule:
Allow 1 credit for ATP/ADP or NADH/NAD.
