Topic: (Nysed) Genetically Modified Organisms
(Nysed) Genetically Modified Organisms
For those individuals who have an allergic reaction to cats, a company in Los Angeles promises relief. They offer a new line of cats genetically modified to eliminate or reduce their allergy-causing properties. The development of this new line of cats most likely involved
(1) using natural selection to produce a new variety of cat
(2) altering the reproductive rate of cats
(3) changing the behavior of cats
(4) manipulating the DNA of cats
Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount of lycopene, a cancer- fighting substance, in tomatoes.
The process of inserting this gene into the DNA of a tomato plant is known as
(1) selective breeding
(2) genetic engineering
(3) cloning
(4) replication
Female mosquitoes spread diseases when they bite humans to obtain blood. It is only the females that do the biting. Research is being conducted to alter the DNA of male mosquitoes. These altered males could then mate with normal female mosquitoes. All of the resulting female offspring would have wing defects that prevent them from flying.
The method used to alter the male mosquitoes is an example of an application of
(1) a feedback mechanism
(2) selective breeding
(3) biotechnology
(4) physiology
Information in segments of human DNA can be expressed by a bacterial cell as a result of
(1) sexual reproduction
(2) random mutation
(3) genetic variability
(4) genetic engineering
Scientists have developed the ability to manufacture hormones, such as human growth hormone, using bacteria. One benefit of this new technology is that
(1) scientists can use only one type of bacteria
(2) bacteria are relatively inexpensive and reproduce quickly
(3) patients can spend more money on their medications
(4) scientists produce drugs that cause more immune reactions
Barley Gene Lowers Emissions From Rice
Over half the people on the planet eat rice as a staple food. Growing rice emits methane, a potent greenhouse gas—to the tune of 25 million to 100 million tons of methane every year, a notable contribution to human-caused greenhouse gas emissions…
…When rice paddies are flooded, methane-producing bacteria thrive on the carbohydrates secreted by rice roots in the oxygen-free soils. The rice plant itself acts as a conduit [pathway], transmitting methane from the soil into the atmosphere…
Source: Times Tribune 7/23/15
Scientists have incorporated a barley gene into a type of rice and produced rice plants that have much lower methane emissions. It is most likely that the scientists incorporated the barley gene into the rice, producing a new variety, using the process of
(1) selective breeding
(2) meiosis, followed by recombination
(3) genetic engineering
(4) sexual reproduction, followed by mitosis
A laboratory technique is represented in the diagram below. Letter A represents a process.

Which specific chemicals are needed to success- fully carry out the process shown at A?
(1) receptor molecules
(2) carbohydrates
(3) enzymes
(4) starch molecules
The diagram below represents a scientific technique in use today.
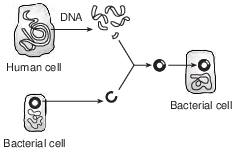
Scientists have used this technique to
(1) produce hormones for human use at a lower cost than other methods
(2) produce pathogens that are able to live in humans
(3) clone human cells with desired characteristics
(4) eliminate the need for laboratory production of medicines for humans
Researchers have produced rice plants that can withstand being completely submerged for up to two weeks. This is good news for farmers in the flood regions of Southeast Asia. The farmers in this region rely heavily on this crop. The diagram below illustrates the process used to genetically modify plants, such as rice.

The best explanation for these modified rice plants being flood resistant is that
(1) the gene for flood resistance was inserted into plant cells, which grew into plants whose cells are expressing this gene
(2) they were produced by fertilization, using gametes from two flood-resistant bacterial cells
(3) there was a mutation in the bacterial DNA after it was inserted into the plant that caused it to be flood resistant
(4) the researchers used selective breeding for the flood-resistance trait
Scientists have been investigating a way to recreate extinct species such as the saber-toothed cat illustrated below.

Which technique would use DNA from an extinct species to recreate an organism of the species?
(1) natural selection
(2) differentiation
(3) cloning
(4) selective breeding
For many years, scientists hypothesized the existence of a single tomato gene that increases the sweetness and production of tomatoes. After years of research, a team of scientists identified the gene and observed greater sweetness and tomato production in plants that contain this gene.
Identify a process that could be used to insert this gene into other plant species to increase fruit production. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — genetic engineering
• — gene splicing
• — gene manipulation
• Note: Do not allow credit for biotechnology; it is a field of science, not a process.
Green Algae Could Help Clean up Radioactive Nuclear Waste
Recent studies have shown that the uses of green algae are boundless. First, scientists at R.I.T. used algae to synthesize biofuel, and recently scientists at Northwestern University and Argonne National have found that freshwater algae can remove strontium 90 from radioactive wastewater. These developments can significantly aid the future effort to clean up radioactive waste at the Fukushima Daichi Plant [a nuclear power plant in Japan]. Scientists discovered that the process begins when the green algae first absorb strontium, calcium and barium from water. The strontium and barium form crystals inside each algae cell. The crystals remain inside the cells, but the algae filters out and excretes calcium and other minerals that may be present. The strontium is then isolated, and thus able to be treated.
Researchers are still figuring the best way to harness the algae’s capabilities. Since algae doesn’t differentiate between radioactive and inactive strontium (they are chemically identical), it is not known how the algae would hold up in a highly radioactive environment. But the good news is that they have been able to manipulate the algae’s process to be more strontium-selective, thus removing as much as possible.…
Source: http://inhabitat.com/green-algae-could-help-clean-up-radioactive-nuclear-waste/algae-ed01/
State one way the scientists may “have been able to manipulate the algae’s process to be more strontium-selective.” [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — They could use genetic engineering to produce algae that are able to collect more
• strontium.
• — gene manipulation
• — Modify their DNA to make them better at taking in the strontium.
• — Find organisms with the specific genes they need, cut them out, and then insert them into
• the algae.
Transgenic Salmon
Transgenic Atlantic salmon have been produced using DNA from other species of related fish. These genetically modified fish have an altered DNA “switch” that causes them to overproduce growth hormone. The transgenic Atlantic salmon grow to normal size, but they reach market size in half the time of conventional Atlantic salmon. As with most of the salmon consumed by people, the transgenic Atlantic salmon would be grown using aquatic farming methods. Scientists have expressed concern that transgenic fish can have undesirable effects on the natural environment. Fish growers would be expected to take steps to ensure that the transgenic salmon do not escape into the wild.
State one advantage genetic modification has over selective breeding when producing new varieties of animals or plants. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — With genetic modification, specific traits can be changed.
• — Direct gene modification can be quicker while selective breeding can take many generations.
• — It can take many generations to modify animals or plants with selective breeding.
Transgenic (GMO) Tomatoes
The use of pesticides to control insects costs billions of dollars every year. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are an attempt to reduce this cost. Tomato plants that are genetically modified can make proteins that are poisonous to the insects that feed on them. Using these GMO tomatoes would reduce the need for the chemical control of insects.
Identify a specific technique used to produce the GMO tomatoes. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — genetic engineering
• — gene splicing
• — genetic manipulation
• Note: Do not accept biotechnology; it is a field of science, not a technique.
Chickens as Drug Factories
Scientists in Scotland have successfully produced five generations of chickens that lay eggs containing certain protein-based drugs. The scientists changed the DNA of the chickens so that two drugs, one used to treat skin cancer and the other used to treat multiple sclerosis, were present in the egg whites. Cows, sheep, and goats have already been altered to produce protein-based drugs in their milk. Chickens are considered good “drug factories” because they are inexpensive to care for, they grow fast, and their chicks inherit the special drug-producing ability.
Explain why scientists altered the DNA of the chickens instead of altering a protein already present in the chickens. In your answer, be sure to:
• identify the technique used to alter the DNA [1]
• state one reason why the scientists altered the DNA of the chickens instead of altering a protein already present in the chickens [1]
• state one advantage of using chickens for this procedure [1]
• state one reason why some people might not support this method of drug production [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 15 Allow 1 credit for identifying the technique used to alter the DNA. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — genetic engineering
• — genetic manipulation
• — gene splicing
• — forming recombinant DNA
• Note: Do not allow credit for biotechnology. It is a field of science, not a technique.
• 16 Allow 1 credit for stating one reason why the scientists altered the DNA of the chickens instead of altering a protein already present in the chickens. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — DNA carries the code for making the proteins.
• — DNA can replicate and the code will be passed on to offspring.
• — Proteins cannot be used to pass on traits.
• — so the chicks will inherit the drug-producing ability
• 17 Allow 1 credit for stating one advantage of using chickens for this procedure. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — They grow fast.
• — They need less room than bigger animals.
• — Chickens are less expensive.
• — Baby chicks inherit the drug-producing ability.
• 18 Allow 1 credit for stating one reason why some people may not support this method of drug production. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — We don’t know the long-term effects of these drugs on the chickens.
• — Some people think products from genetically modified organisms could be harmful.
• — People with egg allergies might not be able to use these drugs.
