Topic: Cells And Protein Functions
Cells And Protein Functions
Diabetes is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. One form of diabetes occurs when insulin fails to properly regulate blood sugar levels. Complications from diabetes can include nerve cell damage and poor blood flow, especially in the feet and legs. In individuals with diabetes, wounds usually take longer than normal to heal.
One reason for the change in wound healing time in a diabetic is that
(1) elevated hormone levels block the synthesis of glucose in immune cells
(2) nerve damage increases absorption of glucose by healthy cells
(3) poor circulation reduces the supply of nutri- ents and oxygen to the cells
(4) decreased enzyme production slows protein synthesis in pancreatic cells
The human body has many cells that are deep inside the body. For this reason, the human body requires
(1) a transport system and other organs
(2) carbon dioxide from the air
(3) the synthesis of many inorganic compounds
(4) the breakdown of glucose by the digestive system
Plant cells can synthesize energy-rich organic molecules, and later break them down to extract that energy for performing life processes. These activities require direct interaction between the
(1) chloroplasts and vacuoles
(2) cell walls and ribosomes
(3) chloroplasts and mitochondria
(4) ribosomes and mitochondria
Which two cell structures work together in the process of protein synthesis?
(1) nucleus and chloroplast
(2) ribosome and vacuole
(3) nucleus and ribosome
(4) mitochondrion and cell membrane
Which observation could lead to the conclusion that an object is nonliving?
(1) It passes on hereditary information only through asexual reproduction.
(2) It carries out synthesis.
(3) It cannot perform metabolic processes.
(4) It is composed of a cell, but does not have tissues.
An ameba is a single-celled, heterotrophic organism. In order to meet its energy needs, it relies directly on the interaction of which cell structures?
(1) chloroplasts and the cell membrane
(2) the cell membrane and mitochondria
(3) nucleus and ribosomes
(4) vacuoles and the nucleus
Anabolic Steroids
Anabolic steroids are hormones that affect muscle growth. Many athletes take synthetic anabolic steroids, in hopes of developing larger muscles so they can perform better at their sport. These hormones can act like the hormone testosterone. When men take an excess of anabolic steroids, they can have an increase in feminine features. This is due to the fact that the excess of these chemicals signals the male body to stop producing testosterone.
This signal in the male body to stop producing testosterone is an example of
(1) an underproduction of estrogen
(2) a feedback mechanism
(3) an overproduction of testosterone
(4) a decrease in anabolic steroid use
Which statement best describes the organelles in a cell?
(1) All organelles are involved directly with communication between cells.
(2) Organelles must work together and their activities must be coordinated.
(3) Organelles function only when there is a dis- ruption in homeostasis.
(4) Each organelle must function independently of the others in order to maintain homeostasis.
Recently, researchers from Stanford University have changed mouse skin cells into mouse nerve cells. This was accomplished by inserting genes that control the synthesis of certain proteins into the skin cells. This type of research is often successful in advancing knowledge regarding the functioning of human cells because
(1) cells present in humans often function in similar ways to cells present in other organisms
(2) cells from different types of organisms function differently when transplanted into humans
(3) the cells in all complex organisms contain the same genes and function in similar ways
(4) cellular research using mice can always be applied to human cells since all complex organisms produce the same proteins
Cell membranes are said to be selectively permeable. Which statement best explains what selectively permeable means?
(1) The cell membrane prevents any harmful substance from entering the cell.
(2) The cell membrane lets certain substances enter the cell and keeps certain substances out of the cell.
(3) The cell membrane allows only large molecules to diffuse into the cell.
(4) The cell membrane has pores that let only water and glucose into the cell and carbon dioxide out.

Which term correctly identifies the process by which molecules move through the dialysis tube membrane?
(1) paper chromatography
(2) active transport
(3) diffusion
(4) digestion
Each body cell contains the same genetic information, but can differ in appearance and size. The diagram below shows three different types of cells found in the human body.

Explain why differences in these human body cells are a biological advantage. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — This allows these cells to be specialized for a specific function.
• — Differences in cells are related to different functions in the body.
The diagram below represents a laboratory setup used to demonstrate the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane.
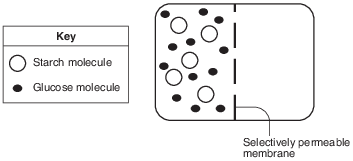
In the diagram below, draw the 5 starch and the 12 glucose molecules to show where they would most likely be located after 15 minutes. [1]

Allow 1 credit for a response showing the five starch molecules only on the left side and glucose
• molecules distributed on both sides.
• Example of a 1-credit response:
• 
• Note: The number of glucose molecules on each side does not have to be equal.
The diagram below represents two types of carbohydrate molecules, glucose and sucrose.

State one reason why a glucose molecule is more likely than a sucrose molecule to diffuse through an artificial membrane. [1].
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The sucrose molecule may be too large to diffuse through the membrane.
• — Glucose is a smaller molecule.
• — Glucose is less complex.

Using information from the diagram, state one reason why the movement of molecules in method C represents active transport. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — C shows the transport of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of higher
• concentration.
• — The molecules are moving against the concentration gradient.
