Topic: Food Web And Cycling Of Matter And Energy In An Ecosystem
Food Web And Cycling Of Matter And Energy In An Ecosystem
Which statement describes an activity of a decomposer?
(1) A mushroom digests and absorbs nutrients from organic matter.
(2) A sunflower uses nutrients from the soil to make proteins.
(3) A snail scrapes algae off rocks in an aquarium.
(4) A hawk eats and digests a mouse.
A relationship between a consumer and producer is best illustrated by a
(1) snake eating a bird
(2) tree absorbing minerals
(3) fungus breaking down wastes
(4) deer eating grass
Euglena are single-celled organisms that live in ponds. All euglena have chloroplasts and can make their own food. They can also take in food from the environment. The diagram below represents a euglena.
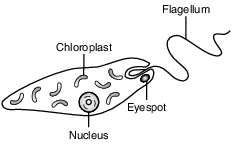
An experiment was set up to determine the effect of nitrates, a pollutant, on the number of chloroplasts present in euglena. Five tanks were set up, each with euglena and a different concentration of nitrate solution: 0%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, and 2.0%.
The tanks were placed in a sunny location where each tank received the same amount of light.
Euglena can be classified as both
(1) an autotroph and a parasite
(2) a decomposer and a heterotroph
(3) a producer and a parasite
(4) an autotroph and a heterotroph
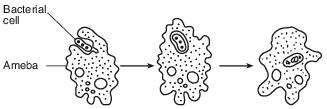
This process represents a step in
(1) asexual reproduction
(2) heterotrophic nutrition
(3) photosynthesis
(4) diffusion
Tracking the Big Horn
Bighorn sheep, Ovis canadensis, are a majestic symbol of the mountainous West. They browse at high altitudes and in steep, rocky areas from Texas to British Columbia. Rams’ horns curl around their eyes and grow up to 45 inches long. Males butt horns to establish dominance during the fall rut [mating season]. Ewes [females] sport shorter, spiked horns similar to a mountain goat’s. From their first days of life, bighorns are surefooted enough to scale cliffs too steep for most predators to follow.…
Two centuries ago, an estimated 1.5 million to 2 million bighorn sheep lived in North America; today, a mere 28,000 remain. Diseases caught from domestic sheep, competition from livestock for forage, and trophy hunting for their horns caused populations to plummet [drop rapidly]. Bighorns graze in mountain meadows, habitat that is being lost to expanding forests, which are growing beyond their historic boundaries in part because the wildfires that are used to hold them in check have been suppressed. Glacier National Park, home to 400 to 600 bighorn sheep, lists the animals as a “species of concern,” that is, at risk of becoming endangered.…
Source: Becky Lomax, Smithsonian Magazine, March, 2008
“Tracking the Big Horn”
The feeding activity of the bighorn sheep is best described as
(1) consumers feeding on autotrophs
(2) decomposers feeding on consumers
(3) autotrophs feeding on decomposers
(4) autotrophs feeding on heterotrophs
Decomposers are necessary in a food chain because they
(1) manufacture food by photosynthesis
(2) return nutrients to the ecosystem
(3) absorb energy from the Sun
(4) produce organic nutrients
Which organisms and set of characteristics are correctly paired?
(1) fungi—carry out photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition
(2) plants—carry out respiration and autotrophic nutrition
(3) decomposers—carry out photosynthesis and autotrophic nutrition
(4) animals—carry out autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition
The diagram below represents a marine food web.

The organisms represented by X are
(1) decomposers
(2) producers
(3) carnivores
(4) scavengers
During certain times of the year, bears feed heavily on a population of fish in a lake. At other times of the year, the bear population feeds primarily on fruits, berries, and insects.
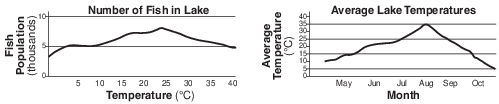
One of the best ways to represent the interdependence of all of the organisms in this ecosystem is
(1) an evolutionary tree
(2) a food chain
(3) an electrophoresis gel
(4) a food web
In a food web, which type of organism receives energy from the other three types?
(1) producer
(2) carnivore
(3) decomposer
(4) herbivore
A corn field includes corn plants, mice, hawks, and various insects, fungi, and bacteria. Which nutritional role is correctly paired with organisms that carry out that role?
(1) heterotrophs – corn and bacteria
(2) producers – insects and fungi
(3) consumers – mice and insects
(4) decomposers – hawks and bacteria
Termites depend on microbes living in their guts to digest molecules of the large, complex carbohydrate, cellulose. Cellulose is the part of wood termites feed on. The microbes produce a substance called cellulase, which speeds up the breakdown of cellulose into molecules of glucose. Termites cannot make cellulase on their own. Without the help of the microbes, the termites are not able to absorb the nutrients that they need to survive.
Explain why the microbes are necessary in order for the termites to absorb nutrients that they need to survive. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Termites cannot digest cellulose, but the microbes can do it for them.
• — The microbes digest the cellulose into glucose, which is small enough to be absorbed by the
• termite.
• — The microbes provide the substance needed to break down the cellulose into glucose.
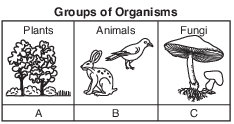
Explain the role of these groups of organisms in the cycling of materials and the transfer of energy in an ecosystem. In your answer, be sure to:
• explain why an ecosystem requires a constant input of energy [1]
• explain how organisms in group B obtain energy [1]
• explain the role of organisms in group C in the ecosystem [1]
• identify the process used by all three groups of organisms to make energy available to their cells to carry out life functions [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 13 Allow 1 credit for explaining why an ecosystem requires a constant input of energy. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Energy is always lost as it is transferred through the ecosystem.
• — Energy is continuously needed for metabolic processes.
• — It is needed so that autotrophs can make food.
• 14 Allow 1 credit for explaining how organisms in group B obtain energy. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Some group B animals eat group A plants.
• — Organisms in group B obtain energy from organisms in group A when they eat them.
• — Group B eats plants, fungi, and/or other animals.
• — The animals eat the plants.
• — They obtain energy from their food.
• 15 Allow 1 credit for explaining the role of organisms in group C in the ecosystem. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Organisms in group C break down dead organisms and return nutrients to the soil.
• — Group C returns raw materials to the ecosystem by decomposing dead organisms.
• — These organisms are decomposers who recycle nutrients in the ecosystem.
• 16 Allow 1 credit for identifying the process used by all three groups of organisms to make energy available to their cells to carry out life functions as respiration or cellular respiration.
The lake sturgeon is a fish that often grows over six feet long and can weigh close to two hundred pounds. It is currently an endangered species in the Great Lakes area, although the species has lived in those lakes and rivers for millions of years. Now, there is a program to increase the sturgeon population by reintroducing lake sturgeon to areas where they have disappeared.
Like the lake sturgeon, bloater fish are also found in the Great Lakes. Both find their food on or near the bottoms of lakes. They eat a variety of small organisms, including insect larvae, worms, and clams. These small organisms feed on algae.
Part of the food web of a lake ecosystem is represented in the diagram below. Indicate the position in the food web where each organism listed below would be placed, by writing the name of each in the appropriate box. [1]

Allow 1 credit for:
• 
Coral Reef Ecosystems
There are many ecological interactions that maintain the biodiversity present in coral reefs. In addition to coral, microscopic algae, seaweed, sea grasses, sponges and worms, and a variety of fish are among the organisms that live in reef ecosystems. Ocean currents often link different reef systems and move organisms from one reef area to another. This movement is a factor in repopulating a reef that has been damaged by environmental changes.
One environmental change involves an increased growth of seaweed. When the population of seaweed increases, the reef shifts from a coral-dominated ecosystem to a seaweed-dominated ecosystem. This change disrupts the relationships between the organisms that live there.
Studies have shown that, as the density of seaweed in a reef area increases, the number of fish that eat the seaweed in that area decreases. This may be due to the presence of more predators, or the taste of the more mature plants. The fish move to areas where there is less seaweed growth. As this trend continues, the reef areas are taken over by the seaweed. Once this happens, it is very hard to remove the seaweed and restore the reef to a healthy ecosystem.
In addition to this problem, temperature changes are threatening the ocean currents that connect the reef systems. A change in the currents would reduce the movement of fish larvae from one area to another. This contributes to the seaweed problem.
State the role of the sea grasses in the reef ecosystem. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Their role is to convert inorganic (raw) materials into organic matter/food.
• — They capture radiant energy.
• — They serve as the producer in this food web/ecosystem.
• — They serve as food for fish.
• — produce oxygen
