Topic: Interdependent Relationships In Ecosystems
Interdependent Relationships In Ecosystems
Which statement best describes what is most likely to occur if an animal population grows larger than the carrying capacity of its environment?
(1) The birth rate will increase.
(2) Both the birth rate and death rate will decrease.
(3) The death rate will increase.
(4) Neither the birth rate nor the death rate will decrease.
The graph below shows the size of a population of foxes over a period of years.
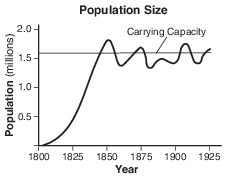
If the line did not stay around the carrying capacity, but continued to rise, which concept would this graph best illustrate?
(1) environmental stability
(2) genetic variety
(3) behavioral change
(4) overproduction
A scientist was studying a population of fish in a pond over a period of 10 years. He observed that the population increased each year for 3 years, and then remained nearly constant for the rest of the study. The best explanation for this observation is that the population had
(1) stopped reproducing
(2) reached carrying capacity
(3) mutated into a different species
(4) run out of food and migrated to a different pond
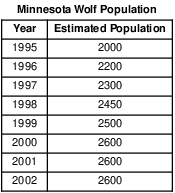
Directions: Using the information in the data table, construct a line graph on the grid, following the directions below.
The most likely explanation for the size of the wolf population for the 2000–2002 period is that the population
(1) reached the carrying capacity of the environment
(2) stabilized due to global warming
(3) began reproducing at a faster rate
(4) was affected by a new pathogen
A finite resource in the environment that keeps a population from steadily increasing is known as
(1) dynamic equilibrium
(2) a limiting factor
(3) a reproductive enzyme
(4) ecological succession
Which statement best describes how a major change in the size of one population affects an ecosystem?
(1) It will immediately affect every population and the physical conditions.
(2) It will affect the physical conditions, but not the other populations.
(3) It could directly or indirectly affect the physical conditions and any population.
(4) It affects every population, not the physical conditions.
The Mississippi River Delta wetlands ecosystem is home to a large number of fish, birds, and other aquatic organisms. During the last century, this ecosystem has seen a decrease in wetland areas and species diversity due to land development, agriculture, and flooding. Conservation groups have been working to reconnect the Mississippi River with its flood plain and restore lost wetlands. One result of restoring wetland areas in this ecosystem would be
(1) an increase in abiotic factors that would cause organisms to develop new adaptations
(2) the development of an ecosystem that will prevent invasive species from settling there
(3) an increase in the carrying capacity of the ecosystem for wetland organisms
(4) to prevent the organisms that live in this eco- system from competing for food and shelter
The number of white-tailed deer in certain areas of Long Island, NY has increased significantly. Homeowners and farmers have put up tall fencing to protect their gardens and crops from the deer. One reason why the white tailed-deer might have increased significantly in certain areas of Long Island is
(1) the lack of natural predators
(2) an increase in deer pathogens
(3) a shortage of biotic resources needed by the deer
(4) that carrying capacity has no effect on deer populations
Many bacteria and fungi are important in the environment because they
(1) return energy to the environment, making it available for plants
(2) recycle nutrients, making them available for other organisms
(3) produce glucose through the process of respiration
(4) reverse the flow of energy in the ecosystem
Which statement best describes a characteristic of the carrying capacity of an ecosystem?
(1) It can be illustrated with a food web.
(2) It allows organisms to produce populations of unlimited size.
(3) It is determined directly by an organism’s reproductive success.
(4) It is limited by the habitat’s available energy and nutrients.
The Eurasian water milfoil is a nonnative species, which was once commonly sold as an aquarium plant, and is now found growing in many lakes in New York State. It has few natural enemies, and grows rapidly, crowding out many native species. This plant ruins fishing areas and interferes with boating and other water sports. This is an example of
(1) human consumption of finite resources
(2) an unintended consequence of adding an organism to an ecosystem
(3) an abiotic factor having a negative effect on an ecosystem
(4) the introduction of a species that has increased the long-term biodiversity of an ecosystem
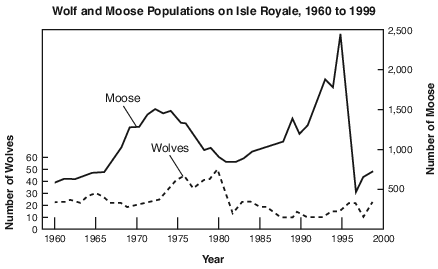
State one possible reason for the change in the moose population between 1995 and 1997. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Disease killed large numbers of the moose.
• — The moose population overgrazed its habitat, resulting in starvation.
• — The moose population exceeded the carrying capacity of the environment.
• — overhunting
• — severe winter
• Note: Do not allow credit for “the wolves ate more moose” or “they died.”
Types of Predators
When large predators, such as lions or wolves, are removed from a food web, smaller “mesopredators” step in to take their places, and the results may be severe. Mesopredators are usually smaller and more numerous than the larger “apex” predators that they replace. Some are also omnivores, eating plant and animal food sources, rather than eating the meat-only diet of the largest predators. Examples of mesopredators include coyotes, raccoons, and skunks.
In 1874, General George Custer noted that there was an abundance of wolves, but few coyotes, in South Dakota. Today, there is an abundance of coyotes, but no wolves. The wolves were removed to protect domestic sheep, but now the coyotes are often responsible for attacking sheep and other animals. The cost of controlling mesopredators by human intervention can be very high, as mesopredators are very numerous and quickly “bounce back” after control efforts. Meanwhile, the number of apex predators that are endangered continues to increase.
Describe how the wolf population is controlled naturally in the environment without human intervention. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The population is controlled by the amount of food available.
• — The population is controlled when too many small animals are eaten and there is a reduced
• amount of food for the wolves.
• — The population is limited by the carrying capacity of the environment.
• — Some die from disease/lack of food.
• — Severe winter may kill some of the wolves.
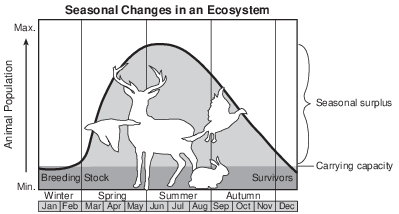
Explain what is meant by the carrying capacity of a particular population in an ecosystem. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals the environment can support over
• an extended period of time.
• — It is the largest population size that can survive in an area year-round.
• — It is the maximum population size that an area’s resources can support.
The graph below shows the carrying capacities of an ecosystem for three different species, 1, 2, and 3, that inhabit an area and the actual population sizes of these three different species in the area.
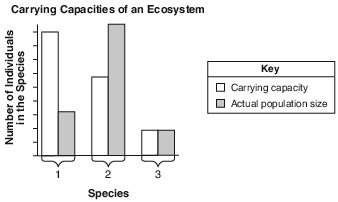
Identify which species population would most likely have the greatest competition among its members. Support your answer using information from the graph. [1]
Species number:_______________________
Allow 1 credit for 2 and supporting the answer. Acceptable responses include, but are not
• limited to:
• — The population size is greater than the size of the population that the ecosystem can
• support.
• — Because it is above its carrying capacity, the ecosystem cannot supply enough food for
• survival, so members of the species compete for limited food.
