Topic: Structural Organization Of Multicellular Organisms
Structural Organization Of Multicellular Organisms
Prions are proteins that act as an infectious agent. They cause a variety of diseases, including “Mad Cow” disease. Prions cannot produce more prions on their own, but cause the host organism to replicate more prions. Most scientists do not consider prions to be alive. A valid reason for accepting that prions are nonliving things is that
(1) no living thing can cause a disease
(2) proteins are inorganic molecules
(3) prions contain all of the material needed to reproduce
(4) prions cannot carry out reproduction independently
The diagram below represents an incomplete sequence of levels of organization.
organelles → tissues → organs → organ systems → organism
This sequence can be completed correctly by inserting
(1) “cells →” between organelles and tissues
(2) “proteins →” between tissues and organs
(3) “populations →” between organs and organ systems
(4) “molecules →” between organ systems and organisms
Which sequence best represents increasing complexity?
(1) tissues → cells → organelles → organs
(2) cells → organelles → organs → organism
(3) organelles → cells → tissues → organs
(4) organism → cells → tissues → organelles
Rabbits have evolved strategies that get them through periods of time when there is little food. The diagram below represents essential life functions that rabbits need to perform.
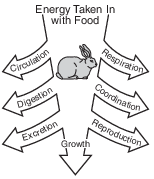
Which life function in the diagram could be eliminated without affecting an individual rabbit’s ability to survive when food is scarce?
(1) digestion
(2) excretion
(3) circulation
(4) reproduction
Bacteria and humans are similar in that they both
(1) contain genetic material
(2) are single-celled
(3) lack cell organelles
(4) carry out autotrophic nutrition
During gas exchange, the cell membrane of a single-celled organism has the same function as which organ system in humans?
(1) nervous
(2) reproductive
(3) digestive
(4) respiratory
Which sequence represents structures organized from least complex to most complex?
(1) nerve cell → nucleus → nervous system → brain
(2) nucleus → nerve cell → brain → nervous system
(3) brain → nervous system → nucleus → nerve cell
(4) nervous system → brain → nerve cell → nucleus
Scientists who study rock formations in caves describe some of the formations as “living rock” because, under certain conditions, they increase in size. Which statement would best dispute the claim that these rock formations are living?
(1) Rocks are not composed of cells, while living organisms are.
(2) Rocks perform complex metabolic processes, but cannot grow.
(3) Rocks cannot reproduce sexually.
(4) Rocks remain stable in a wide range of physical conditions.
Fish absorb oxygen through the gills, earth- worms absorb oxygen through the skin, amebas take in oxygen through the cell membranes, and cows inhale oxygen through the nasal passages into their lungs. This statement demonstrates that living things
(1) rely on similar or the same processes, but accomplish them in different ways
(2) rely on different processes and accomplish them in different ways
(3) rely on different processes, but perform them in the same or related ways
(4) have no relationship to one another, and are all independent individuals
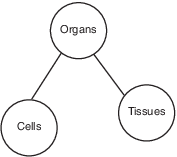
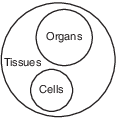
Which diagram best illustrates the relationship between the number of cells, tissues, and organs in a complex multicellular organism?
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 

Which statement correctly identifies the levels of organization for the structures indicated?
(1) A and B are tissues; E and G are organs.
(2) A and B are organs; E and G are systems.
(3) A and B are tissues; E and G are organelles.
(4) A and B are organelles; E and G are organs.
The sequence below represents different organizational levels within the human body, from the simplest to more complex. Complete the sequence by correctly filling in the missing levels. [1]
organelles → ________________ → tissues → ________________ → organ systems → organism
Allow 1 credit for completing the diagram as shown below.
• organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems → organism
Select one row in the chart below and explain how the systems in that row work together during exercise. [1]

Row:
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Row 1:
• — These systems work together to take in and move oxygenated blood to the muscles for use.
• — The respiratory system takes in oxygen, which is passed into the circulatory system, which
• then takes it to the muscles.
• — The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to remove carbon dioxide from the
• muscles.
• Row 2:
• — Muscle cells produce wastes and circulatory transports wastes to excretory organs to be
• excreted.
• Row 3:
• — Digestive breaks down food into nutrients and circulatory transports nutrients to muscle
• cells for energy.
Artificial Placenta
It is estimated that every year more than 15 million babies are born too early. The lungs of these premature infants are often immature and easily damaged. Premature births happen for a variety of reasons—some known and some unknown. Those that are known include infections and conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Scientists are researching what causes premature births, in an attempt to develop solutions to prevent them.
Scientists are also working on the development of an artificial placenta. At the University of Michigan, five premature lambs were placed in artificial placentas and kept alive for weeks. During this time, each lamb’s blood was circulated through its artificial placenta.
Discuss how the development of an artificial placenta is an important step in the study of premature births. In your answer, be sure to:
• explain why it would be harmful for a human mother’s blood to pass across the placenta and into the
fetus [1]
• state how an artificial placenta would be of benefit to the lungs of premature infants [1]
• explain why the lambs’ blood must be filtered as it circulates through the artificial placenta [1]
• state one reason why premature lambs were likely used as model organisms in this study rather than
mice [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 14 Allow 1 credit for stating why it would be harmful for a human mother’s blood to pass across the
• placenta and into the fetus. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The mother’s blood may be interpreted as a pathogen and attacked by the fetus’s immune
• system.
• — The mother’s blood could contain chemicals and pathogens that could harm the fetus.
• — It could cause an immune response.
• — It could be a different blood type that could cause a reaction.
• — It could harm the fetus’s organs.
• 15 Allow 1 credit for describing how an artificial placenta would be of benefit to the lungs of
• premature infants. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The lungs would be able to continue to mature, and the premature infant would not have
• to breathe on its own too soon.
• — The artificial placenta would perform the same processes as the natural placenta, allowing
• the lungs to continue to develop.
• — The artificial placenta would supply oxygen until lungs developed.
• — It would be of benefit because it prevents the accumulation of carbon dioxide.
• — It would help lessen complications associated with the mother’s high blood pressure/
• diabetes.
• 16 Allow 1 credit for explaining why the lambs’ blood must be filtered as it circulates through the
• artificial placenta. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The blood contains waste products that need to be removed.
• — Filtering removes wastes from the blood.
• 17 Allow 1 credit for discussing why premature lambs were likely used as model organisms in this
• study rather than mice. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Lambs are larger and more similar to human fetuses than mice are.
• — The development of a premature lamb is more similar to that of a human.
Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) are associated with some severe human diseases and are inherited through the cytoplasm in the egg cell. These diseases vary, but often affect organs and tissues with the highest energy requirements, including the brain, heart, muscle, pancreas, and kidney.
Scientists have successfully used mitochondrial replacement therapy with monkeys. Scientists are considering using this technique to reduce the incidence of mitochondrial disease in children. The proposed treatment would involve removing the nucleus from an egg donated by a healthy woman and replacing it with an egg nucleus from a patient (mother) with mitochondrial disease. This would place the patient’s egg nucleus into the cytoplasm of the donor’s egg containing healthy mitochondria. The egg is then fertilized with the father’s sperm externally using in vitro fertilization (IVF) to produce a zygote. The zygote is cultured for a few days to produce an embryo.
State one reason why muscle tissues are likely to be affected by mitochondrial diseases. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The mitochondria supply muscles with energy/ATP.
• — If the mitochondria are diseased, they can’t supply the muscle with energy.
• — The mitochondria carry out cell respiration which supplies the muscles with energy.
• — They contain more mitochondria.
• — Muscles have a high energy requirement.
