Topic: Bonding Tendency Of Elements
Bonding Tendency Of Elements
In the formula XF2, the element represented by X can be classified as a
(1) Group 1 metal
(2) Group 2 metal
(3) Group 1 nonmetal
(4) Group 2 nonmetal
Element X reacts with copper to form the compounds CuX and CuX2. In which group on the Periodic Table is element X found?
(1) Group 1
(2) Group 2
(3) Group 13
(4) Group 17
Which statement describes a chemical property of silicon?
(1) Silicon has a blue-gray color.
(2) Silicon is a brittle solid at 20.°C.
(3) Silicon melts at 1414°C.
(4) Silicon reacts with fluorine.
Element X reacts with chlorine to form an ionic compound that has the formula XCl2. To which group on the Periodic Table could element X belong?
(1) Group 1
(2) Group 2
(3) Group 13
(4) Group 15
In the formula for the compound XCl4, the X could represent
(1) C
(2) H
(3) Mg
(4) Zn
In the formula XSO4, the symbol X could represent the element
(1) Al
(2) Ar
(3) Mg
(4) Na
Iron has been used for thousands of years. In the air, iron corrodes. One reaction for the corrosion of iron is represented by the balanced equation below.
Equation 1: 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
In the presence of water, iron corrodes more quickly. This corrosion is represented by the unbalanced equation below.
Equation 2: Fe(s) + O2(g) + H2O(ℓ) → Fe(OH)2(s)
Using equation 1, describe one chemical property of iron.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Iron reacts with oxygen to form a compound.
• An iron atom can lose three electrons.
• The Fe atoms can form positive ions.
The diagram below represents three elements in Group 13 and three elements in Period 3 and their relative positions on the Periodic Table.
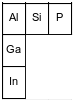
Some elements in the solid phase exist in different forms that vary in their physical properties. For example, at room temperature, red phosphorus has a density of 2.16 g/cm3 and white phosphorus has a density of 1.823 g/cm3.
Identify the element from the diagram that will react with chlorine to form a compound with the general formula XCl4.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Si
• silicon
• element 14
Rubidium and iodine have different chemical and physical properties. Some of these properties are shown in the table below.
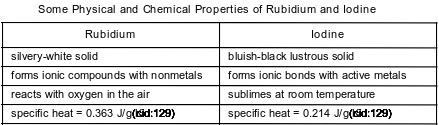
State the chemical property of iodine listed in this table.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• forms ionic bonds with active metals
• forms ionic bonds
• reacts with metals
Three elements, represented by D, E, and Q, are located in Period 3. Some properties of these elements are listed in the table below. A student’s experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is 2.10 g/cm3, at room temperature and standard pressure.
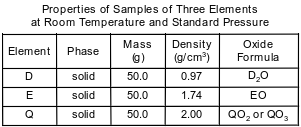
Identify the group on the Periodic Table to which element D belongs.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Group 1
• alkali metals
Some properties of the element sodium are listed below.
- is a soft, silver-colored metal
- melts at a temperature of 371 K
- oxidizes easily in the presence of air
- forms compounds with nonmetallic elements in nature
- forms sodium chloride in the presence of chlorine gas
Identify one chemical property of sodium from this list.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The Na oxidizes easily in the presence of air.
• Sodium reacts with chlorine to form NaCl.
• Sodium forms compounds.
In the late 1800s, Dmitri Mendeleev developed a periodic table of the elements known at that time. Based on the pattern in his periodic table, he was able to predict properties of some elements that had not yet been discovered. Information about two of these elements is shown in the table below.

Write a chemical formula for the compound formed between Ea and Cl.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• EaCl3
• GaCl3
During a fireworks display, salts are heated to very high temperatures. Ions in the salts absorb energy and become excited. Spectacular colors are produced as energy is emitted from the ions in the form of light.
The color of the emitted light is characteristic of the metal ion in each salt. For example, the lithium ion in lithium carbonate, Li2CO3, produces a deep-red color. The strontium ion in strontium carbonate, SrCO3, produces a bright-red color. Similarly, calcium chloride is used for orange light, sodium chloride for yellow light, and barium chloride for green light.
Identify the two types of chemical bonds found in the salt used to produce a deep-red color.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• ionic bonds and polar covalent bonds
• covalent and ionic
Explain, in terms of element classification, why K2O is an ionic compound.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• A metal reacts with a nonmetal to produce an ionic compound.
• Potassium is a metal and oxygen is a nonmetal.
The Lewis electron-dot diagrams for three substances are shown below.

Describe, in terms of valence electrons, how the chemical bonds form in the substance represented in diagram 1.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Valence electrons are lost by potassium and gained by bromine.
• The ions form as a result of a transfer of electrons between the atoms.
