Topic: Characteristic Trends
Characteristic Trends
Which atom in the ground state has an outer- most electron with the most energy?
(1) Cs
(2) K
(3) Li
(4) Na
The valence electron of which atom in the ground state has the greatest amount of energy?
(1) cesium
(2) lithium
(3) rubidium
(4) sodium
Which general trends in first ionization energy and electronegativity values are demonstrated by Group 15 elements as they are considered in order from top to bottom?
(1) The first ionization energy decreases and the electronegativity decreases.
(2) The first ionization energy increases and the electronegativity increases.
(3) The first ionization energy decreases and the electronegativity increases.
(4) The first ionization energy increases and the electronegativity decreases.
In the ground state, an atom of each of the elements in Group 2 has a different
(1) oxidation state
(2) first ionization energy
(3) number of valence electrons
(4) number of electrons in the first shell
Which group on the Periodic Table has two elements that exist as gases at STP?
(1) Group 1
(2) Group 2
(3) Group 16
(4) Group 17
Which trend is observed as the first four elements in Group 17 on the Periodic Table are considered in order of increasing atomic number?
(1) Electronegativity increases.
(2) First ionization energy decreases.
(3) The number of valence electrons increases.
(4) The number of electron shells decreases.
Which atom has the largest atomic radius?
(1) potassium
(2) rubidium
(3) francium
(4) cesium
Which property decreases when the elements in Group 17 are considered in order of increasing atomic number?
(1) atomic mass
(2) atomic radius
(3) melting point
(4) electronegativity
Which ion has the largest radius?
(1) Br−
(2) Cl−
(3) F−
(4) I−
The atomic radius and the ionic radius for some Group 1 and some Group 17 elements are given in the tables below.

Explain, in terms of electron shells, why the radius of a K+ ion is greater than the radius of an Na+ ion.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• A K+ ion has three electron shells and an Na+ ion has only two.
• A sodium ion has fewer electron shells than a potassium ion.
There are six elements in Group 14 on the Periodic Table. One of these elements has the symbol Uuq, which is a temporary, systematic symbol. This element is now known as flerovium.
Explain, in terms of electron shells, why each successive element in Group 14 has a larger atomic radius, as the elements are considered in order of increasing atomic number.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The atomic radius of these elements increases down the group because each successive element has one more electron shell.
• The number of shells per atom increases.
The elements in Group 17 are called halogens. The word “halogen” is derived from Greek and means “salt former.”
State the trend in electronegativity for the halogens as these elements are considered in order of increasing atomic number.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As atomic number increases, electronegativity decreases.
• Electronegativity decreases.
Many scientists made observations of the elements that led to the modern Periodic Table. In 1829, Dobereiner found groups of three elements that have similar properties and called each of these groups a triad. Dobereiner noticed a relationship between the atomic masses of the elements in each triad. Triad 1, shown in the table below, consists of sulfur, selenium, and tellurium. The middle element, selenium, has an atomic mass that is close to the sum of the atomic masses of sulfur and tellurium, divided by 2.

The other triads shown in the table below demonstrate the same mathematical relationship.

State the trend in first ionization energy as the elements in triad 3 are considered in order of increasing atomic number.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As the atomic number increases, the first ionization energy decreases.
• The first ionization energy decreases.
The elements in Group 2 on the Periodic Table can be compared in terms of first ionization energy, electronegativity, and other general properties.
Describe the general trend in electronegativity as the metals in Group 2 on the Periodic Table are considered in order of increasing atomic number.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Electronegativity generally decreases as the metals in Group 2 are considered in order of increasing atomic number.
• Electronegativity decreases.
Radioactive emissions can be detected by a Geiger counter. When radioactive emissions enter the Geiger counter probe, which contains a noble gas such as argon or helium, some of the atoms are ionized. The ionized gas allows for a brief electric current. The current causes the speaker to make a clicking sound. To make sure that the Geiger counter is measuring radiation properly, the device is tested using the radioisotope Cs-137.
To detect gamma radiation, an aluminum shield can be placed over the probe window, to keep alpha and beta radiation from entering the probe. A diagram that represents the Geiger counter is shown below.
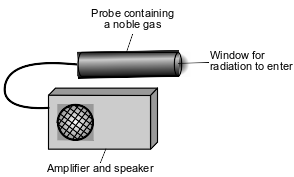
Compare the first ionization energy of argon to the first ionization energy of helium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Argon has a lower ionization energy than helium.
• The Ar has a first ionization energy of 1521 kJ/mol and the He has a first ionization energy of 2372 kJ/mol.
• Helium has a higher first ionization energy than argon.
