Topic: Chemical Bonding
Chemical Bonding
Chemical properties can be used to
(1) determine the temperature of a substance
(2) determine the density of a substance
(3) differentiate between two compounds
(4) differentiate between two neutrons
Compared to the physical and chemical proper- ties of the compound NO2, the compound N2O has
(1) different physical properties and different chemical properties
(2) different physical properties and the same chemical properties
(3) the same physical properties and different chemical properties
(4) the same physical properties and the same chemical properties
Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide have
(1) the same chemical properties and the same physical properties
(2) the same chemical properties and different physical properties
(3) different chemical properties and the same physical properties
(4) different chemical properties and different physical properties
Which statement describes H2O(ℓ) and H2O2(ℓ)?
(1) Both are compounds that have the same properties.
(2) Both are compounds that have different properties.
(3) Both are mixtures that have the same properties.
(4) Both are mixtures that have different properties.
A sample of a substance has these characteristics: (cid:129) melting point of 984 K (cid:129) hard, brittle solid at room temperature (cid:129) poor conductor of heat and electricity as a solid (cid:129) good conductor of electricity as a liquid or in
an aqueous solution
This sample is classified as
(1) a metallic element
(2) a radioactive element
(3) a molecular compound
(4) an ionic compound
Which formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound?
(1) N2 and SO2
(2) Cl2 and H2S
(3) BaCl2 and N2O4
(4) NaOH and BaSO4
Compared to the chemical and physical properties of the compound CO, the compound CO2 has
(1) the same chemical properties and the same physical properties
(2) the same chemical properties and different physical properties
(3) different chemical properties and the same physical properties
(4) different chemical properties and different physical properties
A 2.5 L sample of SO2(g) at STP and a 2.5 L sample of CO2(g) at STP can be differentiated by comparing their
(1) masses
(2) phases
(3) temperatures
(4) volumes
Which property can be used to differentiate between a 50.-gram sample of solid potassium nitrate at STP and a 50.-gram sample of solid silver chloride at STP?
mL
(1) mass
(2) temperature
(3) phase
(4) solubility
A laboratory technician is given the table below and a sample of one of the three substances listed in the table. The technician makes an aqueous solution with a portion of the sample. When a conductivity tester is lowered into the solution, the lightbulb on the tester glows brightly. Another portion of the sample is placed in a heat-resistant container that is placed in an oven at 450.°C. The sample melts.

Identify the substance given to the technician.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• sodium nitrate
• NaNO3
Some compounds of silver are listed with their chemical formulas in the table below.
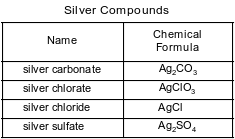
Explain, in terms of element classification, why silver chloride is an ionic compound.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The reaction between a metal and a nonmetal can produce an ionic compound.
• Silver is a metal and chlorine is a nonmetal.
A student drew the Lewis electron-dot diagram below to represent sodium chloride.

Explain why this diagram is not an accurate representation for the bonding in NaCl.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Ion charges are not shown.
• No electron transfer is shown in the diagram.
• The student’s diagram represents a molecular compound.
Rubidium and iodine have different chemical and physical properties. Some of these properties are shown in the table below.
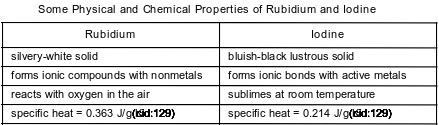
State the chemical property of iodine listed in this table.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• forms ionic bonds with active metals
• forms ionic bonds
• reacts with metals
During a fireworks display, salts are heated to very high temperatures. Ions in the salts absorb energy and become excited. Spectacular colors are produced as energy is emitted from the ions in the form of light.
The color of the emitted light is characteristic of the metal ion in each salt. For example, the lithium ion in lithium carbonate, Li2CO3, produces a deep-red color. The strontium ion in strontium carbonate, SrCO3, produces a bright-red color. Similarly, calcium chloride is used for orange light, sodium chloride for yellow light, and barium chloride for green light.
Identify the two types of chemical bonds found in the salt used to produce a deep-red color.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• ionic bonds and polar covalent bonds
• covalent and ionic
The Lewis electron-dot diagrams for three substances are shown below.

Describe, in terms of valence electrons, how the chemical bonds form in the substance represented in diagram 1.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Valence electrons are lost by potassium and gained by bromine.
• The ions form as a result of a transfer of electrons between the atoms.
