Topic: Chemical Bonds
Chemical Bonds
Element X reacts with chlorine to form an ionic compound that has the formula XCl2. To which group on the Periodic Table could element X belong?
(1) Group 1
(2) Group 2
(3) Group 13
(4) Group 15
An ionic bond can be formed when one or more electrons are
(1) equally shared by two atoms
(2) unequally shared by two atoms
(3) transferred from the nucleus of one atom to the nucleus of another atom
(4) transferred from the valence shell of one atom to the valence shell of another atom
In the compound KHSO4, there is an ionic bond between the
(1) KH+ and SO42− ions + and O2− ions
(2) KHSO3
(3) K+ and HS− ions − ions
(4) K+ and HSO4
When lithium reacts with bromine to form the compound LiBr, each lithium atom
(1) gains one electron and becomes a negatively charged ion
(2) gains three electrons and becomes a negatively charged ion
(3) loses one electron and becomes a positively charged ion
(4) loses three electrons and becomes a positively charged ion
Which element reacts with oxygen to form ionic bonds?
(1) calcium
(2) hydrogen
(3) chlorine
(4) nitrogen
Given the formula for hydrazine:
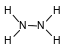
How many pairs of electrons are shared between the two nitrogen atoms?
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
At STP, which substance has metallic bonding?
(1) ammonium chloride
(2) barium oxide
(3) iodine
(4) silver
Which type of bonding is present in a sample of an element that is malleable?
(1) ionic
(2) metallic
(3) nonpolar covalent
(4) polar covalent
Rubidium and iodine have different chemical and physical properties. Some of these properties are shown in the table below.
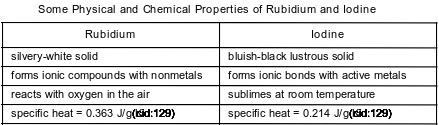
State the chemical property of iodine listed in this table.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• forms ionic bonds with active metals
• forms ionic bonds
• reacts with metals
During a fireworks display, salts are heated to very high temperatures. Ions in the salts absorb energy and become excited. Spectacular colors are produced as energy is emitted from the ions in the form of light.
The color of the emitted light is characteristic of the metal ion in each salt. For example, the lithium ion in lithium carbonate, Li2CO3, produces a deep-red color. The strontium ion in strontium carbonate, SrCO3, produces a bright-red color. Similarly, calcium chloride is used for orange light, sodium chloride for yellow light, and barium chloride for green light.
Identify the two types of chemical bonds found in the salt used to produce a deep-red color.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• ionic bonds and polar covalent bonds
• covalent and ionic
The Lewis electron-dot diagrams for three substances are shown below.

Describe, in terms of valence electrons, how the chemical bonds form in the substance represented in diagram 1.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Valence electrons are lost by potassium and gained by bromine.
• The ions form as a result of a transfer of electrons between the atoms.
Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for a molecule of hydrogen fluoride, HF.
Allow 1 credit.
• Examples of 1-credit responses:
• chem12018-rg_g1.png
The formulas and names of four chloride compounds are shown in the table below.
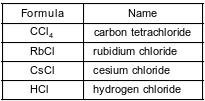
Explain, in terms of atomic structure, why the radius of a cesium ion in cesium chloride is smaller than the radius of a cesium atom when both are in the ground state.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• A cesium atom loses its valence electron, making the cesium ion smaller.
• The cesium atom has one more electron shell than the cesium ion.
• A Cs+ ion has only 5 shells of electrons in the ground state and the Cs atom has 6 shells.
A thiol is very similar to an alcohol, but a thiol has a sulfur atom instead of an oxygen atom in the functional group. The equation below represents a reaction of methanethiol and iodine, producing dimethyl disulfide and hydrogen iodide.
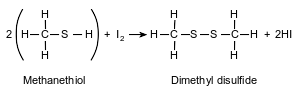
State the number of electrons shared between the sulfur atoms in the dimethyl disulfide.
Allow 1 credit for 2 or two or 1 pair.
When magnesium is ignited in air, the magnesium reacts with oxygen and nitrogen. The reaction between magnesium and nitrogen is represented by the unbalanced equation below.
Mg(s) + N2(g) → Mg3N2(s)
Explain, in terms of electrons, why an atom of the metal in this reaction forms an ion that has a smaller radius than its atom.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• An atom of magnesium loses its outer shell electrons to form the Mg2+ ion.
• The electron configuration of a magnesium atom is 2-8-2, and the electron configuration of the magnesium ion is 2-8.
• An atom of the metal loses electrons to form the ion.
