Topic: Collision Theory And The Rate Of Reaction
Collision Theory And The Rate Of Reaction
What is required for a chemical reaction to occur?
(1) standard temperature and pressure
(2) a catalyst added to the reaction system
(3) effective collisions between reactant particles
(4) an equal number of moles of reactants and products
Two hydrogen atoms form a hydrogen molecule when
(1) one atom loses a valence electron to the other atom
(2) one atom shares four electrons with the other atom
(3) the two atoms collide and both atoms gain energy
(4) the two atoms collide with sufficient energy to form a bond
A reaction will most likely occur if the colliding particles have the proper
(1) mass, only
(2) mass and volume
(3) orientation, only
(4) orientation and energy
A chemical reaction is most likely to occur when the colliding particles have the proper
(1) energy and orientation
(2) solubility and density
(3) ionic radii and mass
(4) atomic radii and volume
According to which theory or law is a chemical reaction most likely to occur when two particles with the proper energy and orientation interact with each other?
(1) atomic theory
(2) collision theory
(3) combined gas law
(4) law of conservation of matter
An effective collision between reactant particles requires the particles to have the proper
(1) charge and mass
(2) charge and orientation
(3) energy and mass
(4) energy and orientation
In the laboratory, a student investigates the effect of concentration on the reaction between HCl(aq) and Mg(s), changing only the concentration of HCl(aq). Data for two trials in the investigation are shown in the table below.
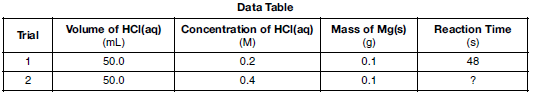
Compared to trial 1, what is the expected reaction time for trial 2 and the explanation for that result?
(1) less than 48 s, because there are fewer effective particle collisions per second
(2) less than 48 s, because there are more effective particle collisions per second
(3) more than 48 s, because there are fewer effective particle collisions per second
(4) more than 48 s, because there are more effective particle collisions per second
The collision theory states that a reaction is most likely to occur when the reactant particles collide with the proper
(1) formula masses
(2) molecular masses
(3) density and volume
(4) energy and orientation
A chemical reaction occurs when reactant particles
(1) are separated by great distances
(2) have no attractive forces between them
(3) collide with proper energy and proper orientation
(4) convert chemical energy into nuclear energy
Which statement explains why increasing the temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction, while other conditions remain the same?
(1) The reacting particles have less energy and collide less frequently.
(2) The reacting particles have less energy and collide more frequently.
(3) The reacting particles have more energy and collide less frequently.
(4) The reacting particles have more energy and collide more frequently.
Several steps are involved in the industrial production of sulfuric acid. One step involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide gas to form sulfur trioxide gas. A catalyst is used to increase the rate of production of sulfur trioxide gas. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, this reaction reaches equilibrium, as represented by the equation below.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) + 392 kJ
Explain, in terms of collision theory, why increasing the pressure of the gases in the cylinder increases the rate of the forward reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• When the pressure in the cylinder is increased, the SO2(g) molecules and O2(g) molecules collide more frequently, producing more SO3(g).
Carbon monoxide, CO(g), is a toxic gas found in automobile exhaust. The concentration of CO(g) can be decreased by using a catalyst in the reaction between CO(g) and O2(g). This reaction is represented by the balanced equation below.

Explain, in terms of collision theory, why an increase in temperature increases the rate of the reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The rate of the chemical reaction increases because the reactant molecules move faster and collide with more kinetic energy.
• Increasing the temperature causes more frequent collisions.
• As molecules acquire more kinetic energy, the probability of effective collisions increases.
• More reactant molecules collide with sufficient energy.
Methanol can be manufactured by a reaction that is reversible. In the reaction, carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas react using a catalyst. The equation below represents this system at equilibrium.
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g) + energy
Explain, in terms of collision theory, why increasing the concentration of H2(g) in this system will increase the concentration of CH3OH(g).
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• More H2(g) molecules collide with CO(g) molecules, producing more CH3OH(g).
• Adding H2 increases the number of effective collisions to produce more methanol.
• A greater number of effective collisions occur.
Millions of tons of ammonia are produced each year for use as fertilizer to increase food production. Most of the hydrogen needed to produce ammonia comes from methane gas reacting with steam. This reaction, which occurs in a container under controlled conditions, is shown below in unbalanced equation 1.
Equation 1: CH4(g) + H2O(g) + energy → CO(g) + H2(g)
The reaction that produces ammonia is represented by balanced equation 2, shown below. A catalyst can be used to increase the rate of the reaction.
Equation 2: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) + energy
A potential energy diagram for equation 2 is shown below.
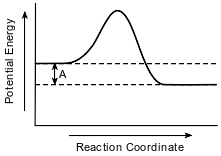
Explain, in terms of collision theory, why an increase in temperature increases the rate of reaction between methane gas and steam.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• An increase in temperature causes a greater number of effective collisions between methane and water molecules to occur.
• A greater number of collisions per second make the reaction rate faster.
• More molecules collide with sufficient energy.
Explain, in terms of collisions, why increasing the surface area of the hot carbon increases the rate of the forward reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Increasing the surface area of the hot carbon increases the frequency of effective collisions, which increases the rate of the forward reaction.
• More collisions between C atoms and H2O molecules speed up the reaction.
• More effective collisions occur.
