Topic: Equilibrium
Equilibrium
Some solid KNO3 remains at the bottom of a stoppered flask containing a saturated KNO3(aq) solution at 22°C. Which statement explains why the contents of the flask are at equilibrium?
(1) The rate of dissolving is equal to the rate of crystallization.
(2) The rate of dissolving is greater than the rate of crystallization.
(3) The concentration of the solid is equal to the concentration of the solution.
(4) The concentration of the solid is greater than the concentration of the solution.
Which type of equilibrium exists in a sealed flask containing Br2(ℓ) and Br2(g) at 298 K and 1.0 atm?
(1) static phase equilibrium
(2) static solution equilibrium
(3) dynamic phase equilibrium
(4) dynamic solution equilibrium
At which temperature will Hg(ℓ) and Hg(s) reach equilibrium in a closed system at 1.0 atmosphere?
(1) 234 K
(2) 273 K
(3) 373 K
(4) 630. K
Equilibrium can be reached by
(1) physical changes, only
(2) nuclear changes, only
(3) both physical changes and chemical changes
(4) both nuclear changes and chemical changes
An open flask is half filled with water at 25°C. Phase equilibrium can be reached after
(1) more water is added to the flask
(2) the flask is stoppered
(3) the temperature is decreased to 15°C
(4) the temperature is increased to 35°C
Which changes can reach dynamic equilibrium?
(1) nuclear changes, only
(2) chemical changes, only
(3) nuclear and physical changes
(4) chemical and physical changes
Which equation represents a chemical equilibrium?
(1) N2(ℓ) ⇌ N2(g)
(2) 2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g)
(3) CO2(s) ⇌ CO2(g)
(4) NH3(ℓ) ⇌ NH3(g)
A cube of iron at 20.°C is placed in contact with a cube of copper at 60.°C. Which statement describes the initial flow of heat between the cubes?
(1) Heat flows from the copper cube to the iron cube.
(2) Heat flows from the iron cube to the copper cube.
(3) Heat flows in both directions between the cubes.
(4) Heat does not flow between the cubes.
Which equation represents a physical equilibrium?
(1) 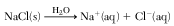
(2) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ O2(g) + 2SO3(g)
(3) 3O2(g) → 2O3(g)
(4) N2(ℓ) ⇌ N2(g)
Which statement describes a chemical reaction at equilibrium?
(1) The products are completely consumed in the reaction.
(2) The reactants are completely consumed in the reaction.
(3) The concentrations of the products and reactants are equal.
(4) The concentrations of the products and reactants are constant.
Common household bleach is an aqueous solution containing hypochlorite ions. A closed container of bleach is an equilibrium system represented by the equation below.
Cl2(g) + 2OH−(aq) ⇌ ClO−(aq) + Cl−(aq) + H2O(ℓ)
Compare the rate of the forward reaction to the rate of the reverse reaction for this system.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
• They are the same.
• equal
A student makes an aqueous solution of lactic acid. A formula for one form of lactic acid is shown below.
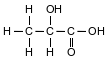
The solution is placed in a sealed flask to be used in a laboratory investigation. The equation below represents the lactic acid equilibrium system in the flask.

Explain, in terms of the reaction rates, why the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant in this system.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
• The reaction rates are the same at equilibrium.
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2, is a dark brown gas that is used to make nitric acid and to bleach flour. Nitrogen dioxide has a boiling point of 294 K at 101.3 kPa. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, nitrogen dioxide can be in equilibrium with colorless dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4. This equilibrium is represented by the equation below.
2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) + 58 kJ
Compare the rate of the forward reaction to the rate of the reverse reaction when the system has reached equilibrium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction at equilibrium.
• The rates are the same.
The balanced equation below represents the reaction between a 5.0-gram sample of zinc metal and a 0.5 M solution of hydrochloric acid. The reaction takes place in an open test tube at 298 K and 1 atm in a laboratory activity.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) + energy
Explain why this reaction will not reach equilibrium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The H2(g) can leave the open test tube.
• The reaction is driven to completion because a gas is released.
• Reaction not reversible.
In a laboratory apparatus, a sample of lead(II) oxide reacts with hydrogen gas at high temperature. The products of this reaction are liquid lead and water vapor. As the reaction proceeds, water vapor and excess hydrogen gas leave the glass tube. The diagram and balanced equation below represent this reaction.
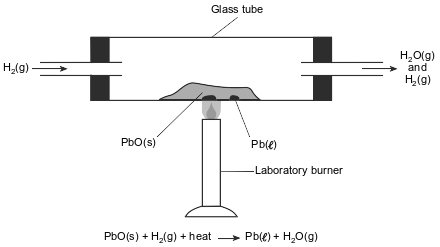
Explain why the reaction that occurs in this glass tube can not reach equilibrium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The glass tube is not a closed system.
• Gases are entering and leaving the system.
