Topic: Functional Groups And Types Of Organic Compounds
Functional Groups And Types Of Organic Compounds
Functional groups are used to classify
(1) organic compounds
(2) inorganic compounds
(3) heterogeneous mixtures
(4) homogeneous mixtures
Which class of compounds contains at least one element from Group 17 of the Periodic Table?
(1) aldehyde
(2) amine
(3) ester
(4) halide
Which class of organic compounds contains nitrogen?
(1) aldehyde
(2) alcohol
(3) amine
(4) ether
An alcohol and an ether have the same molecular formula, C2H6O. These two compounds have
(1) the same functional group and the same physical and chemical properties
(2) the same functional group and different physical and chemical properties
(3) different functional groups and the same physical and chemical properties
(4) different functional groups and different physical and chemical properties
The compounds CH3OCH3 and CH3CH2OH have different functional groups. Therefore, these compounds have different
(1) chemical properties
(2) gram-formula masses
(3) percent compositions by mass
(4) numbers of atoms per molecule
Which atom is bonded to the carbon atom in the functional group of a ketone?
(1) fluorine
(2) hydrogen
(3) nitrogen
(4) oxygen
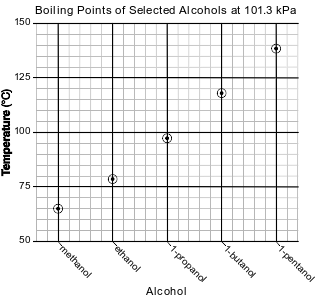
What is represented by the number “1” in the IUPAC name for three of these alcohols?
(1) the number of isomers for each alcohol
(2) the number of −OH groups for each carbon atom in each alcohol molecule
(3) the location of an −OH group on one end of the carbon chain in each alcohol molecule
(4) the location of an −OH group in the middle of the carbon chain in each alcohol molecule
The active ingredient in the pain reliever aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid. This compound can be produced by reacting salicylic acid with acetic acid. The label of one aspirin bottle indicates that the accepted mass of acetylsalicylic acid in each tablet is 325 milligrams.
In a laboratory, an aspirin tablet is crushed and mixed with water to dissolve all of the acetylsalicylic acid. The measured pH of the resulting solution is 3.0.
Write the chemical formula for the acetic acid.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• HC2H3O2(aq)
• CH3COOH
In one method of making bread, starch is broken down into glucose. Zymase, an enzyme present in yeast, acts as a catalyst for the reaction in which the glucose reacts to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide gas causes the bread dough to rise. The balanced equation below represents the catalyzed reaction.
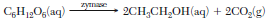
Identify the functional group in an ethanol molecule.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• −OH
• alcohol group
• Note: Do not allow credit for hydroxide or OH−.
Table sugar, sucrose, is a combination of two simple sugars, glucose and fructose. The formulas below represent these simple sugars.

Identify the functional group that appears more than once in the fructose molecule.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• –OH
• OH
• alcohol
• hydroxyl
• hydroxy group
• Note: Do not allow credit for hydroxide ion or hydroxyl radical or OH−.
Rubbing alcohol is a product available at most pharmacies and supermarkets. One rubbing alcohol solution contains 2-propanol and water. The boiling point of 2-propanol is 82.3°C at standard pressure.
Draw a structural formula for the 2-propanol.
Allow 1 credit.
• Examples of 1-credit responses:
• chem12014-rg_g2.png
A student makes an aqueous solution of lactic acid. A formula for one form of lactic acid is shown below.
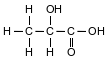
The solution is placed in a sealed flask to be used in a laboratory investigation. The equation below represents the lactic acid equilibrium system in the flask.

Identify one organic functional group in a molecule of lactic acid.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• chem12015-rg_g4.png
Molecules containing two carbon atoms and a functional group have many home and industrial uses. These compounds can be produced by a variety of reactions, as shown by the equations below.
Equation 1: C2H4 + H2O → CH3CH2OH
Equation 2: 2CH3CH2OH + O2 → 2CH3CHO + 2H2O
Equation 3: 2CH3CHO + O2 → 2CH3COOH
Draw a structural formula of the ethanal molecule in equation 2.
Allow 1 credit.
• Examples of 1-credit responses:
• chem12017-rg_g8.png
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a polymer used to make drain pipes, flooring, electric wire insulation, and some plastic bottles. Making PVC requires several reactions. The first step is represented by the equation below.

The 1,2-dichloroethane is converted to vinyl chloride. To produce PVC, the vinyl chloride monomer is polymerized, as represented by the equation below.

Identify the class of organic compounds to which the product of equation 1 belongs.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• halide
• halocarbons
• alkyl halide
• halogenoalkane
One type of soap is produced when ethyl stearate and sodium hydroxide react. The soap produced by this reaction is called sodium stearate. The other product of the reaction is ethanol. This reaction is represented by the balanced equation below.
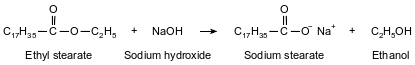
To which class of organic compounds does ethyl stearate belong?
Allow 1 credit for ester or esters.
