Topic: Gas Lows
Gas Lows
At 25°C, gas in a rigid cylinder with a movable piston has a volume of 145 mL and a pressure of 125 kPa. Then the gas is compressed to a volume of 80. mL. What is the new pressure of the gas if the temperature is held at 25°C?
(1) 69 kPa
(2) 93 kPa
(3) 160 kPa
(4) 230 kPa
A 220.0-mL sample of helium gas is in a cylinder with a movable piston at 105 kPa and 275 K. The piston is pushed in until the sample has a volume of 95.0 mL. The new temperature of the gas is 310. K. What is the new pressure of the sample?
(1) 51.1 kPa
(2) 216 kPa
(3) 243 kPa
(4) 274 kPa
A sample of chlorine gas is at 300. K and 1.00 atmosphere. At which temperature and pressure would the sample behave more like an ideal gas?
(1) 0 K and 1.00 atm
(2) 150. K and 0.50 atm
(3) 273 K and 1.00 atm
(4) 600. K and 0.50 atm
When a sample of a gas is heated in a sealed, rigid container from 200. K to 400. K, the pressure exerted by the gas is
(1) decreased by a factor of 2
(2) increased by a factor of 2
(3) decreased by a factor of 200.
(4) increased by a factor of 200.
Under which conditions of temperature and pressure does a real gas behave most like an ideal gas?
(1) low temperature and low pressure
(2) low temperature and high pressure
(3) high temperature and low pressure
(4) high temperature and high pressure
A rigid cylinder with a movable piston contains a sample of gas. At 300. K, this sample has a pressure of 240. kilopascals and a volume of 70.0 milliliters. What is the volume of this sample when the temperature is changed to 150. K and the pressure is changed to 160. kilopascals?
(1) 35.0 mL
(2) 52.5 mL
(3) 70.0 mL
(4) 105 mL
A rigid cylinder with a movable piston contains a sample of hydrogen gas. At 330. K, this sample has a pressure of 150. kPa and a volume of 3.50 L. What is the volume of this sample at STP?
(1) 0.233 L
(2) 1.96 L
(3) 4.29 L
(4) 6.26 L
Which unit is used to express the pressure of a gas?
(1) mole
(2) joule
(3) kelvin
(4) pascal
A sample of helium gas is in a sealed, rigid container. What occurs as the temperature of the sample is increased?
(1) The mass of the sample decreases.
(2) The number of moles of gas increases.
(3) The volume of each atom decreases.
(4) The frequency of collisions between atoms increases.
The diagram below represents a cylinder with a movable piston. The cylinder contains 1.0 liter of oxygen gas at STP. The movable piston in the cylinder is pushed downward at constant temperature until the volume of O2(g) is 0.50 liter.
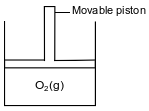
Determine the new pressure of O2(g) in the cylinder, in atmospheres.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
The diagram and data below represent a gas and the conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas in a rigid cylinder with a moveable piston.
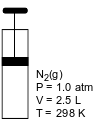
Determine the volume of the gas in the cylinder at STP.
Allow 1 credit for 2.3 L or for any value from 2.29 L to 2.3 L, inclusive.
A bubble of air at the bottom of a lake rises to the surface of the lake. Data for the air inside the bubble at the bottom of the lake and at the surface of the lake are listed in the table below.

State the number of significant figures used to express the pressure at the surface of the lake.
Allow 1 credit for 4 or four.
In a laboratory activity, the volume of helium gas in a rigid cylinder with a movable piston is varied by changing the temperature of the gas. The activity is done at a constant pressure of 100. kPa. Data from the activity are plotted on the graph below.
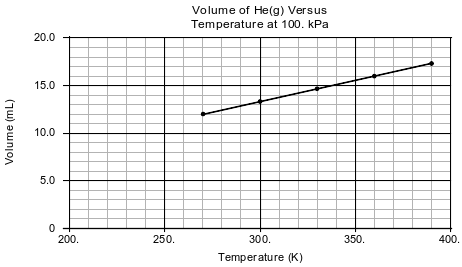
Determine the temperature of the He(g) at a volume of 15.0 mL.
Allow 1 credit for any value from 334 K to 341 K, inclusive.
At standard pressure, hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, melts at −0.4°C, boils at 151°C, and is very soluble in water. A bottle of aqueous hydrogen peroxide, H2O2(aq), purchased from a pharmacy has a pressure-releasing cap. Aqueous hydrogen peroxide decomposes at room temperature, as represented by the balanced equation below.
2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(ℓ) + O2(g) + 196.0 kJ
Explain why a hydrogen peroxide bottle needs a pressure-releasing cap.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The excess pressure due to the production of oxygen gas in the bottle needs to be gradually released.
• As O2(g) is produced, the pressure inside of the bottle might increase and the bottle might burst without the pressure-releasing cap.
Cylinder A has a movable piston and contains hydrogen gas. An identical cylinder, B, contains methane gas. The diagram below represents these cylinders and the conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas in each cylinder.
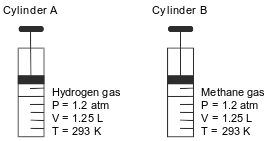
State a change in temperature and a change in pressure that will cause the gas in cylinder A to behave more like an ideal gas.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Temperature: above 293 K. Pressure: below 1.2 atm
• Temperature: higher. Pressure: lower
