Topic: Heat And Temperature
Heat And Temperature
Given the cooling curve of a substance:

During which intervals is potential energy decreasing and average kinetic energy remaining constant?
(1) AB and BC
(2) AB and CD
(3) DE and BC
(4) DE and EF
A beaker with water and the surrounding air are all at 24°C. After ice cubes are placed in the water, heat is transferred from
(1) the ice cubes to the air
(2) the beaker to the air
(3) the water to the ice cubes
(4) the water to the beaker
The graph below represents the relationship between time and temperature as heat is added at a constant rate to a sample of a substance.

During interval AB, which energy change occurs for the particles in this sample?
(1) The potential energy of the particles increases.
(2) The potential energy of the particles decreases.
(3) The average kinetic energy of the particles increases.
(4) The average kinetic energy of the particles decreases.
Which unit is used to express an amount of thermal energy?
(1) gram
(2) mole
(3) joule
(4) pascal
The heating curve below represents a sample of a substance starting as a solid below its melting point and being heated over a period of time.

Which statement describes the energy of the particles in this sample during interval DE?
(1) Both potential energy and average kinetic energy increase.
(2) Both potential energy and average kinetic energy decrease.
(3) Potential energy increases and average kinetic energy remains the same.
(4) Potential energy remains the same and average kinetic energy increases.
Given samples of water:
Sample 1: 100. grams of water at 10.°C Sample 2: 100. grams of water at 20.°C
Compared to sample 1, sample 2 contains
(1) molecules with a lower average kinetic energy
(2) molecules with a lower average velocity
(3) less heat energy
(4) more heat energy
The cooling curve below represents the uniform cooling of a substance, starting at a temperature above its boiling point.
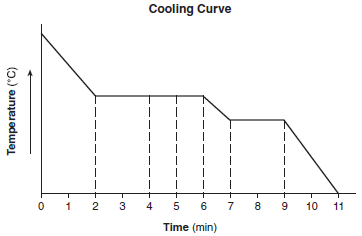
During which time interval does the substance exist as both a liquid and a solid?
(1) min 2 to min 4
(2) min 4 to min 5
(3) min 5 to min 7
(4) min 7 to min 9
Which type of energy is associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules in a sample of air?
(1) chemical energy
(2) electrical energy
(3) nuclear energy
(4) thermal energy
Starting as a gas at 206°C, a sample of a substance is allowed to cool for 16 minutes. This process is represented by the cooling curve below.

What is the melting point of this substance?
Allow 1 credit for 90°C ± 2°C.
A student investigated heat transfer using a bottle of water. The student placed the bottle in a room at 20.5°C. The student measured the temperature of the water in the bottle at 7 a.m. and again at 3 p.m. The data from the investigation are shown in the table below.

State the direction of heat transfer between the surroundings and the water in the bottle from 7 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Heat was transferred from the surroundings to the water in the bottle.
• The water absorbed energy from the surroundings.
The compounds KNO3 and NaNO3 are soluble in water.
Explain why the total thermal energy of a sample containing 22.2 grams of NaNO3 dissolved in 200. grams of water at 20.°C is greater than the total thermal energy of a sample containing 11.1 grams of NaNO3 dissolved in 100. grams of water at 20.°C.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Both samples are at 20.°C, but the larger sample has more matter.
• The larger sample has twice as many particles.
• The total thermal energy is directly proportional to the masses of the samples.
The formulas and the boiling points at standard pressure for ethane, methane, methanol, and water are shown in the table below.

State the change in potential energy that takes place in a sample of methane as it boils at −161.5°C.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As liquid methane boils, the potential energy of the sample increases.
• Potential energy increases.
A student made a copper bracelet by hammering a small copper bar into the desired shape. The bracelet has a mass of 30.1 grams and was at a temperature of 21°C in the classroom. After the student wore the bracelet, the bracelet reached a temperature of 33°C. Later, the student removed the bracelet and placed it on a desk at home, where it cooled from 33°C to 19°C. The specific heat capacity of copper is 0.385 J/g•K.
Explain, in terms of heat flow, the change in the temperature of the bracelet when the student wore the bracelet.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The bracelet temperature increased because heat flowed from the body to the copper.
• Energy is tranferred from the student to the bracelet.
• Heat is absorbed by the bracelet.
Carbon dioxide, CO2, changes from the solid phase to the gas phase at 1 atm and 194.5 K. In the solid phase, CO2 is often called dry ice. When dry ice sublimes in air at 298 K, the water vapor in the air can condense, forming a fog of small water droplets. This fog is often used for special effects at concerts and in movie-making.
State the direction of heat flow between the dry ice and the water vapor in the air.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• from water vapor to the dry ice
• from H2O(g) to CO2(s)
• from water to CO2
Thermal energy is absorbed as chemical reactions occur during the process of baking muffins. The batter for muffins often contains baking soda, NaHCO3(s), which decomposes as the muffins are baked in an oven at 200.°C. The balanced equation below represents this reaction, which releases CO2(g) and causes the muffins to rise as they bake. The H2O(ℓ) is released into the air of the oven as it becomes a vapor.
2NaHCO3(s) + heat → Na2CO3(s) + H2O(ℓ) + CO2(g)
State the direction of heat flow between the air in the oven and the muffin batter when the muffin batter is first placed in the preheated oven at 200.°C.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• from oven air to muffin batter
• from air to muffin
• from air to batter
