Topic: Historic Models
Historic Models
As a result of the gold foil experiment, it was concluded that an atom
(1) contains protons, neutrons, and electrons
(2) contains a small, dense nucleus
(3) has positrons and orbitals
(4) is a hard, indivisible sphere
Given a list of atomic model descriptions:
A: electron shells outside a central nucleus B: hard, indivisible sphere C: mostly empty space
Which list of atomic model descriptions represents the order of historical development from the earliest to most recent?
(1) A, B, C
(2) A, C, B
(3) B, C, A
(4) B, A, C
The results of the gold foil experiment led to the conclusion that an atom is
(1) mostly empty space and has a small, negatively charged nucleus
(2) mostly empty space and has a small, positively charged nucleus
(3) a hard sphere and has a large, negatively charged nucleus
(4) a hard sphere and has a large, positively charged nucleus
Which conclusion was drawn from the results of the gold foil experiment?
(1) An atom is electrically neutral.
(2) An atom is mostly empty space.
(3) The nucleus of an atom is negatively charged.
(4) The electrons in an atom are located in specific shells.
Four statements about the development of the atomic model are shown below.
A: Electrons have wavelike properties. B: Atoms have small, negatively charged particles. C: The center of an atom is a small, dense nucleus. D: Atoms are hard, indivisible spheres.
Which order of statements represents the historical development of the atomic model?
(1) C → D → A → B
(2) C → D → B → A
(3) D → B → A → C
(4) D → B → C → A
The discovery of the electron as a subatomic particle was a result of
(1) collision theory
(2) kinetic molecular theory
(3) the gold-foil experiment
(4) experiments with cathode ray tubes
Which statement describes the earliest model of the atom?
(1) An atom is an indivisible hard sphere.
(2) An atom has a small, dense nucleus.
(3) Electrons are negative particles in an atom.
(4) Electrons in an atom have wave-like properties.
Which subatomic particles were discovered as the result of experiments with cathode ray tubes?
(1) electrons
(2) neutrons
(3) positrons
(4) protons
Which conclusion was developed as a result of the gold foil experiment?
(1) Atoms are mostly empty space.
(2) All atoms are hard, indivisible spheres.
(3) Atoms have different volumes.
(4) All atoms have the same volume.
Which conclusion directly resulted from the “gold foil experiment”?
(1) Atoms are mostly empty space.
(2) Atoms are hard, indivisible spheres.
(3) Electrons are located in shells.
(4) Electrons have a small mass.
Which proposal in the development of the modern model of the atom was made before the others?
(1) Atoms are hard, indivisible spheres of different sizes.
(2) Atoms are mostly empty space with a small dense nucleus.
(3) Atoms have electrons that have wavelike properties.
(4) Atoms have an internal structure that contains negative particles.
Before atomic numbers were known, Mendeleev developed a classification system for the 63 elements known in 1872, using oxide formulas and atomic masses. He used an R in the oxide formulas to represent any element in each group. The atomic mass was listed in parentheses after the symbol of each element. A modified version of Mendeleev’s classification system is shown in the table below.
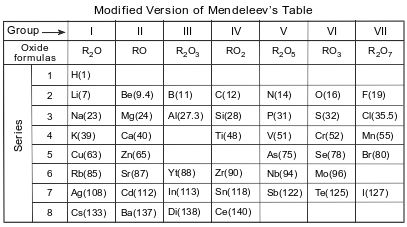
Identify one characteristic used by Mendeleev to develop his classification system of the elements.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• increasing atomic mass
• atomic mass
• oxide formulas
A student compares some models of the atom. These models are listed in the table below in order of development from top to bottom.
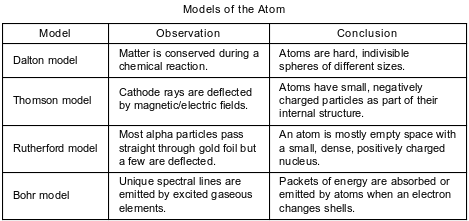
State the model that first included electrons as subatomic particles.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Thomson model
• Thomson
• plum pudding model
In the late 1800s, Dmitri Mendeleev developed a periodic table of the elements known at that time. Based on the pattern in his periodic table, he was able to predict properties of some elements that had not yet been discovered. Information about two of these elements is shown in the table below.

Identify the element that Mendeleev called eka-silicon, Es.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Ge
• germanium
Many scientists made observations of the elements that led to the modern Periodic Table. In 1829, Dobereiner found groups of three elements that have similar properties and called each of these groups a triad. Dobereiner noticed a relationship between the atomic masses of the elements in each triad. Triad 1, shown in the table below, consists of sulfur, selenium, and tellurium. The middle element, selenium, has an atomic mass that is close to the sum of the atomic masses of sulfur and tellurium, divided by 2.

The other triads shown in the table below demonstrate the same mathematical relationship.

Show a numerical setup that demonstrates Dobereiner’s mathematical relationship for triad 2.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• chem82017-rg_g1.png
