Topic: Intermolecular Forces And Physical Properties Of Substances
Intermolecular Forces And Physical Properties Of Substances
According to Table F, which ions combine with chloride ions to form an insoluble compound?
(1) Fe2+ ions
(2) Ca2+ ions
(3) Li+ ions
(4) Ag+ ions
Which element has the highest boiling point at standard pressure?
(1) Mg
(2) Na
(3) Rb
(4) Sr
Based on Table F, which compound is least soluble in water?
(1) AlPO4
(2) Li2SO4
(3) Ca(OH)2
(4) AgC2H3O2
Compared to a 1.0-mole sample of NaCl(s), a 1.0-mole sample of NaCl(ℓ) has a different
(1) number of ions
(2) empirical formula
(3) gram-formula mass
(4) electrical conductivity
At standard pressure, CH4 boils at 112 K and H2O boils at 373 K. What accounts for the higher boiling point of H2O at standard pressure?
(1) covalent bonding
(2) ionic bonding
(3) hydrogen bonding
(4) metallic bonding
At which temperature is the vapor pressure of ethanol equal to 80. kPa?
(1) 48°C
(2) 73°C
(3) 80.°C
(4) 101°C
The formulas and the boiling points at standard pressure for ethane, methane, methanol, and water are shown in the table below.

Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why the solubility of methanol in water is greater than the solubility of methane in water.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Methanol and water molecules are polar, but methane molecules are nonpolar.
• The compounds methanol and water have similar polarities.
A solution of ethylene glycol and water can be used as the coolant in an engine-cooling system. The ethylene glycol concentration in a coolant solution is often given as percent by volume. For example, 100. mL of a coolant solution that is 40.% ethylene glycol by volume contains 40. mL of ethylene glycol diluted with enough water to produce a total volume of 100. mL. The graph below shows the freezing point of coolants that have different ethylene glycol concentrations.
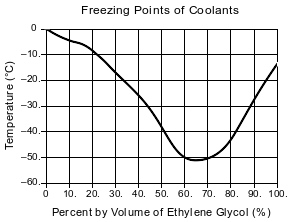
Explain, in terms of the molecular polarity, why ethylene glycol dissolves in water to form a solution.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable response include, but are not limited to:
• Water molecules and ethylene glycol molecules are both polar.
• Water and the glycol have similar polarities.
Chemical concepts are applied in candy making. A recipe for making lollipops is shown below.

Explain, in terms of the polarity of sugar molecules, why the sugar dissolves in water.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The polarity of sugar molecules is similar to the polarity of water molecules.
• Both substances consist of polar molecules.
At standard pressure, water has unusual properties that are due to both its molecular structure and intermolecular forces. For example, although most liquids contract when they freeze, water expands, making ice less dense than liquid water. Water has a much higher boiling point than most other molecular compounds having a similar gram-formula mass.
Explain why H2O(s) floats on H2O(ℓ) when both are at 0ºC.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• When water freezes it expands, making H2O(s) less dense than H2O(ℓ).
• The distance between the H2O molecules is greater in the solid phase.
• The density of liquid water is greater.
• The density of ice is less.
The unique odors and flavors of many fruits are primarily due to small quantities of a certain class of organic compounds. The equation below represents the production of one of these compounds.

Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why reactant 2 is soluble in water.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Both water and methanoic acid have polar molecules.
• Both molecules are polar.
• Polar dissolves polar.
• Reactant 2 molecules and the water molecules have similar polarities.
Carbon dioxide is slightly soluble in seawater. As carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere increase, more CO2 dissolves in seawater, making the seawater more acidic because carbonic acid, H2CO3(aq), is formed.
Seawater also contains aqueous calcium carbonate, CaCO3(aq), which is used by some marine organisms to make their hard exoskeletons. As the acidity of the sea water changes, the solubility of CaCO3 also changes, as shown in the graph below.
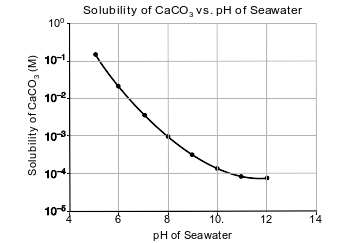
State the trend in the solubility of CaCO3 as seawater becomes more acidic.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As the seawater becomes more acidic, the solubility of CaCO3 increases.
• As the pH of the seawater decreases, the solubility of calcium carbonate increases.
• solubility increases
• more soluble
Hydrazine, N2H4, is a compound that is very soluble in water and has a boiling point of 113°C at standard pressure. Unlike water, hydrazine is very reactive and is sometimes used as a fuel for small rockets. One hydrazine reaction producing gaseous products is represented by the balanced equation below.
N2H4(ℓ) → N2(g) + 2H2(g) + heat
Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why the boiling point of hydrazine at standard pressure is higher than the boiling point of water at standard pressure.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The intermolecular forces in hydrazine must be greater than the intermolecular forces in water.
• The intermolecular forces in H2O are weaker.
There are several isomers of C6H14. The formulas and boiling points for two of these isomers are given in the table below.
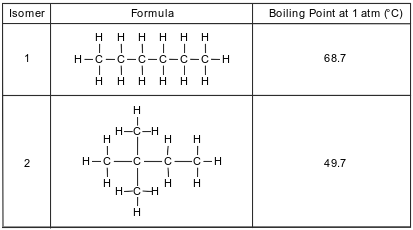
Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why isomer 2 boils at a lower temperature than isomer 1.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Isomer 2 boils at a lower temperature because it has weaker intermolecular forces than isomer 1.
• The intermolecular forces in isomer 1 are stronger.
Ethane, C2H6, has a boiling point of −89°C at standard pressure. Ethanol, C2H5OH, has a much higher boiling point than ethane at standard pressure. At STP, ethane is a gas and ethanol is a liquid.
Compare the intermolecular forces of the two substances at STP.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Ethane has weaker intermolecular forces (IMF) than ethanol.
• Ethanol has hydrogen bonding.
• Van der Waals forces are weaker in C2H6.
