Topic: Isotopes Atomic Mass
Isotopes Atomic Mass
The numbers of protons and neutrons in each of four different atoms are shown in the table below.
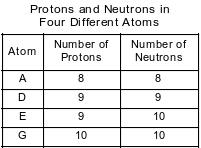
Which two atoms represent isotopes of the same element?
(1) A and D
(2) A and G
(3) E and D
(4) E and G
The nuclides I-131 and I-133 are classified as
(1) isomers of the same element
(2) isomers of Xe-131 and Cs-133
(3) isotopes of the same element
(4) isotopes of Xe-131 and Cs-133
The three nuclides, U-233, U-235, and U-238, are isotopes of uranium because they have the same number of protons per atom and
(1) the same number of electrons per atom
(2) the same number of neutrons per atom
(3) a different number of electrons per atom
(4) a different number of neutrons per atom
An atom that has 13 protons and 15 neutrons is an isotope of the element
(1) nickel
(2) silicon
(3) aluminum
(4) phosphorus
If two atoms are isotopes of the same element, the atoms must have
(1) the same number of protons and the same number of neutrons
(2) the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons
(3) a different number of protons and the same number of neutrons
(4) a different number of protons and a different number of neutrons
Which notations represent atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons?
(1) H-3 and He-3
(2) S-32 and S-32
(3) Cl-35 and Cl-37
(4) Ga-70 and Ge-73
Which phrase describes two atoms that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons?
(1) ions of the same element
(2) isotopes of the same element
(3) a mixture of different elements
(4) nuclides of different elements
Two atoms that are different isotopes of the same element have
(1) the same number of protons and the same number of neutrons
(2) the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
(3) a different number of protons but the same number of neutrons
(4) a different number of protons and a different number of neutrons
Iodine has many isotopes, but only iodine-127 is stable and is found in nature. One radioactive iodine isotope, I-108, decays by alpha particle emission. Iodine-131 is also radioactive and has many important medical uses.
Explain, in terms of protons and neutrons, why I-127 and I-131 are different isotopes of iodine.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• I-127 atoms and I-131 atoms have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
• Both have 53 p, but I-127 has 74 n while I-131 has 78 n.
• They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
• same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons
• The only difference is the number of neutrons.
The diagram below shows the first three steps in the uranium-238 radioactive decay series.
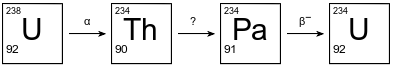
The decay mode for the first and third steps is shown above the arrows. The decay mode for the second step is not shown in the diagram. Thorium-234 has a half-life of 24.10 days.
Explain, in terms of neutrons and protons, why U-238 and U-234 are different isotopes of uranium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• An atom of U-238 has 92 protons and 146 neutrons. An atom of U-234 also has 92 protons but has 142 neutrons.
• These two atoms have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
Some isotopes of neon are Ne-19, Ne-20, Ne-21, Ne-22, and Ne-24. The neon-24 decays by beta emission. The atomic mass and natural abundance for the naturally occurring isotopes of neon are shown in the table below.

State the number of neutrons in an atom of Ne-20 and the number of neutrons in an atom of Ne-22.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Ne-20: 10____
• Ne-22: 12____
Illuminated EXIT signs are used in public buildings such as schools. If the word EXIT is green, the sign may contain the radioisotope tritium, hydrogen-3. The tritium is a gas sealed in glass tubes. The emissions from the decay of the tritium gas cause a coating on the inside of the tubes to glow.
State, in terms of neutrons, how an atom of tritium differs from an atom of hydrogen-1.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• A tritium atom has two neutrons and an H-1 atom has no neutrons.
• Only the tritium atom has neutrons.
• H-1 has no neutrons.
The diagrams below represent four different atomic nuclei.
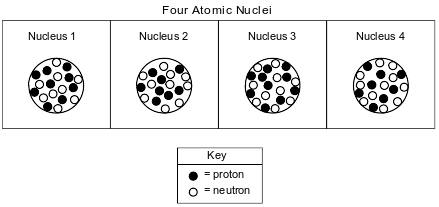
Explain why nucleus 2 and nucleus 4 represent the nuclei of two different isotopes of the same element.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Both have 8 protons, but nucleus 2 has 10 neutrons while nucleus 4 has 11 neutrons.
• equal in protons, unequal in neutrons
• same atomic number, but different mass number
Cobalt-60 is an artificial isotope of Co-59. The incomplete equation for the decay of cobalt-60, including beta and gamma emissions, is shown below.

Explain, in terms of both protons and neutrons, why Co-59 and Co-60 are isotopes of cobalt.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Both atoms have 27 protons, but Co-59 atoms each have 32 neutrons and Co-60 atoms each have 33 neutrons.
• same number of protons, different number of neutrons
The table below shows data for three isotopes of the same element.
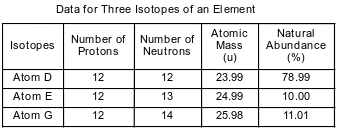
Explain, in terms of subatomic particles, why these three isotopes represent the same element.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Atoms of isotopes D, E and G have the same number of protons.
• They each have 12 protons.
