Topic: Kinetic Molecular Theory (Kmt)
Kinetic Molecular Theory (Kmt)
Which statement describes the particles of an ideal gas according to the kinetic molecular theory?
(1) The gas particles are arranged in a regular geometric pattern.
(2) The gas particles are in random, constant, straight-line motion.
(3) The gas particles are separated by very small distances, relative to their sizes.
(4) The gas particles are strongly attracted to each other.
According to the kinetic molecular theory, which statement describes the particles of an ideal gas?
(1) The gas particles are arranged in a regular pattern.
(2) The force of attraction between the gas particles is strong.
(3) The gas particles are hard spheres in continuous circular motion.
(4) The collisions of the gas particles may result in the transfer of energy.
According to the kinetic molecular theory for an ideal gas, all gas particles
(1) are in random, constant, straight-line motion
(2) are separated by very small distances relative to their sizes
(3) have strong intermolecular forces
(4) have collisions that decrease the total energy of the system
The kinetic molecular theory states that all particles of an ideal gas are
(1) colliding without transferring energy
(2) in random, constant, straight-line motion
(3) arranged in a regular geometric pattern
(4) separated by small distances relative to their size
Which statement describes the particles of an ideal gas, based on the kinetic molecular theory?
(1) The motion of the gas particles is orderly and circular.
(2) The gas particles have no attractive forces between them.
(3) The gas particles are larger than the dis- tances separating them.
(4) As the gas particles collide, the total energy of the system decreases.
According to the kinetic molecular theory, which statement describes an ideal gas?
(1) The gas particles are diatomic.
(2) Energy is created when the gas particles collide.
(3) There are no attractive forces between the gas particles.
(4) The distance between the gas particles is small, compared to their size.
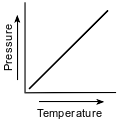
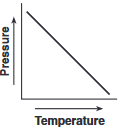
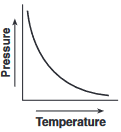
Which graph shows the relationship between pressure and Kelvin temperature for an ideal gas at constant volume?
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Which phrase describes the motion and attractive forces of ideal gas particles?
(1) random straight-line motion and no attractive forces
(2) random straight-line motion and strong attractive forces
(3) random curved-line motion and no attractive forces
(4) random curved-line motion and strong attractive forces
Which statement describes the particles of an ideal gas, based on the kinetic molecular theory?
(1) The volume of the particles is considered negligible.
(2) The force of attraction between the particles is strong.
(3) The particles are closely packed in a regular, repeating pattern.
(4) The particles are separated by small distances, relative to their size.
According to kinetic molecular theory, collisions between gas particles in a sample of an ideal gas
(1) increase the energy content of the gas sample
(2) produce strong attractive forces between the gas particles
(3) result in a net loss of energy by the gas sample
(4) transfer energy between the gas particles
Which statement describes particles of an ideal gas, based on the kinetic molecular theory?
(1) Gas particles are separated by distances smaller than the size of the gas particles.
(2) Gas particles do not transfer energy to each other when they collide.
(3) Gas particles have no attractive forces between them.
(4) Gas particles move in predictable, circular motion.
According to kinetic molecular theory, which statement describes one characteristic of an ideal gas system?
(1) The distance between gas molecules is smaller than the diameter of one gas molecule.
(2) The attractive force between two gas molecules is strong.
(3) The energy of the system decreases as gas molecules collide.
(4) The straight-line motion of the gas molecules is constant and random.
According to the kinetic molecular theory, which statement describes the particles in a sample of an ideal gas?
(1) The particles are constantly moving in circular paths.
(2) The particles collide, decreasing the total energy of the system.
(3) The particles have attractive forces between them.
(4) The particles are considered to have negligible volume.
In a laboratory activity, the volume of helium gas in a rigid cylinder with a movable piston is varied by changing the temperature of the gas. The activity is done at a constant pressure of 100. kPa. Data from the activity are plotted on the graph below.
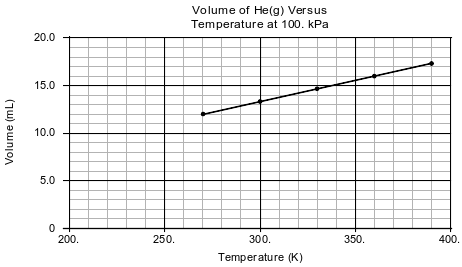
Explain, in terms of particle volume, why the sample of helium can not be compressed by the piston to zero volume.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Unlike ideal gas particles, He particles have volume.
• Each atom of helium occupies space.
A sample of helium gas is placed in a rigid cylinder that has a movable piston. The volume of the gas is varied by moving the piston, while the temperature is held constant at 273 K. The volumes and corresponding pressures for three trials are measured and recorded in the data table below. For each of these trials, the product of pressure and volume is also calculated and recorded. For a fourth trial, only the volume is recorded.

Compare the average distances between the helium atoms in trial 1 to the average distances between the helium atoms in trial 3.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The average distance between helium atoms is smaller in trial 1 than in trial 3.
• In trial 3, the atoms are farther apart.
• The separation is greater in trial 3.
• Atoms are closer in trial 1.
• The smaller the volume, the closer the gas molecules.
