Topic: Lechatelier'S Principle
Lechatelier'S Principle
For a reaction at equilibrium, which change can increase the rates of the forward and reverse reactions?
(1) a decrease in the concentration of the reactants
(2) a decrease in the surface area of the products
(3) an increase in the temperature of the system
(4) an increase in the activation energy of the forward reaction
Which term identifies a factor that will shift a chemical equilibrium?
(1) atomic radius
(2) catalyst
(3) decay mode
(4) temperature
Given the equation representing a system at equilibrium:

When the concentration of Cl−(aq) is increased, the concentration of Ag+(aq)
(1) decreases, and the amount of AgCl(s) increases
(2) decreases, and the amount of AgCl(s) decreases
(3) increases, and the amount of AgCl(s) increases
(4) increases, and the amount of AgCl(s) decreases
Given the equation representing a reaction at equilibrium:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) + heat
Which change causes the equilibrium to shift to the right?
(1) adding a catalyst
(2) adding more O2(g)
(3) decreasing the pressure
(4) increasing the temperature
Given the equation representing a system at equilibrium:
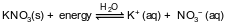
Which change causes the equilibrium to shift?
(1) increasing pressure
(2) increasing temperature
(3) adding a noble gas
(4) adding a catalyst
Given the equation representing a chemical reaction at equilibrium in a sealed, rigid container:
H2(g) + I2(g) + energy ⇌ 2HI(g)
When the concentration of H2(g) is increased by adding more hydrogen gas to the container at constant temperature, the equilibrium shifts
(1) to the right, and the concentration of HI(g) decreases
(2) to the right, and the concentration of HI(g) increases
(3) to the left, and the concentration of HI(g) decreases
(4) to the left, and the concentration of HI(g) increases
Given the equation representing a system at equilibrium:
PCl5(g) + energy ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
Which change will cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
(1) adding a catalyst
(2) adding more PCl3(g)
(3) increasing the pressure
(4) increasing the temperature
Several steps are involved in the industrial production of sulfuric acid. One step involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide gas to form sulfur trioxide gas. A catalyst is used to increase the rate of production of sulfur trioxide gas. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, this reaction reaches equilibrium, as represented by the equation below.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) + 392 kJ
State, in terms of the concentration of SO3(g), what occurs when more O2(g) is added to the reaction at equilibrium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The concentration of SO3(g) increases.
Common household bleach is an aqueous solution containing hypochlorite ions. A closed container of bleach is an equilibrium system represented by the equation below.
Cl2(g) + 2OH−(aq) ⇌ ClO−(aq) + Cl−(aq) + H2O(ℓ)
Explain why the container must be closed to maintain equilibrium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The container must be closed so that no matter can enter or leave, thus disturbing the equilibrium.
• If the container is open, Cl2 gas escapes.
• to keep the concentrations of the reactants and products constant
A student makes an aqueous solution of lactic acid. A formula for one form of lactic acid is shown below.
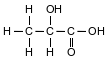
The solution is placed in a sealed flask to be used in a laboratory investigation. The equation below represents the lactic acid equilibrium system in the flask.

Explain, in terms of LeChatelier’s principle, why increasing the concentration of H+(aq) increases the concentration of lactic acid.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The stress of adding H+ ions shifts the equilibrium to the left, producing more lactic acid.
• Increasing the concentration of H+(aq) favors the reverse reaction.
• More H+ ions collide with lactate ions, shifting the equilibrium left.
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2, is a dark brown gas that is used to make nitric acid and to bleach flour. Nitrogen dioxide has a boiling point of 294 K at 101.3 kPa. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, nitrogen dioxide can be in equilibrium with colorless dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4. This equilibrium is represented by the equation below.
2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) + 58 kJ
State one stress, other than adding or removing NO2(g) or N2O4(g), that would increase the amount of the dark brown gas.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Increase the temperature.
• Add heat.
• Decrease the pressure.
• Increase the volume.
The balanced equation below represents the reaction between a 5.0-gram sample of zinc metal and a 0.5 M solution of hydrochloric acid. The reaction takes place in an open test tube at 298 K and 1 atm in a laboratory activity.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) + energy
Explain why this reaction will not reach equilibrium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The H2(g) can leave the open test tube.
• The reaction is driven to completion because a gas is released.
• Reaction not reversible.
In a laboratory apparatus, a sample of lead(II) oxide reacts with hydrogen gas at high temperature. The products of this reaction are liquid lead and water vapor. As the reaction proceeds, water vapor and excess hydrogen gas leave the glass tube. The diagram and balanced equation below represent this reaction.
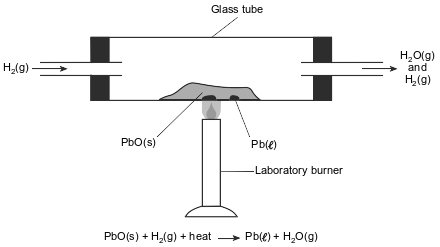
Explain why the reaction that occurs in this glass tube can not reach equilibrium.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The glass tube is not a closed system.
• Gases are entering and leaving the system.
The equation below represents an equilibrium system of SO2(g), O2(g), and SO3(g). The reaction can be catalyzed by vanadium or platinum.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) + energy
State how the equilibrium shifts when SO3(g) is removed from the system.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The equilibrium will shift to favor the formation of SO3.
• The rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
• The equilibrium will shift to favor the forward reaction.
• The equilibrium will shift to the right.
• The concentrations of the reactants will decrease.
Stamping an identification number into the steel frame of a bicycle compresses the crystal structure of the metal. If the number is filed off, there are scientific ways to reveal the number.
One method is to apply aqueous copper(II) chloride to the number area. The Cu2+ ions react with some iron atoms in the steel frame, producing copper atoms that show the pattern of the number. The ionic equation below represents this reaction.
Fe(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Another method is to apply hydrochloric acid to the number area. The acid reacts with the iron, producing bubbles of hydrogen gas. The bubbles form faster where the metal was compressed, so the number becomes visible. The equation below represents this reaction.
2HCl(aq) + Fe(s) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Describe one change in the HCl(aq) that will increase the rate at which hydrogen bubbles are produced when the acid is applied to the steel frame.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Increase the concentration of the HCl(aq).
• Increase the temperature.
