Topic: Properties In A Group
Properties In A Group
Which list includes elements with the most similar chemical properties?
(1) Br, Ga, Hg
(2) Cr, Pb, Xe
(3) O, S, Se
(4) N, O, F
Which element has chemical properties that are most similar to the chemical properties of fluorine?
(1) boron
(2) chlorine
(3) neon
(4) oxygen
The elements in Group 2 have similar chemical properties because each atom of these elements has the same
(1) atomic number
(2) mass number
(3) number of electron shells
(4) number of valence electrons
Which elements have the most similar chemical properties?
(1) boron and carbon
(2) oxygen and sulfur
(3) aluminum and bromine
(4) argon and silicon
The number of valence electrons in each atom of an element affects the element’s
(1) chemical properties
(2) number of isotopes
(3) decay mode
(4) half-life
In the ground state, all atoms of Group 15 elements have the same number of
(1) valence electrons
(2) electron shells
(3) neutrons
(4) protons
Which elements have the most similar chemical properties?
(1) Si, As, and Te
(2) N2, O2, and F2
(3) Mg, Sr, and Ba
(4) Ca, Cs, and Cu
Chlorine and element X have similar chemical properties. An atom of element X could have an electron configuration of
(1) 2-2
(2) 2-8-1
(3) 2-8-8
(4) 2-8-18-7
The diagram below represents three elements in Group 13 and three elements in Period 3 and their relative positions on the Periodic Table.
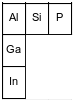
Some elements in the solid phase exist in different forms that vary in their physical properties. For example, at room temperature, red phosphorus has a density of 2.16 g/cm3 and white phosphorus has a density of 1.823 g/cm3.
Identify one element from the diagram that will combine with phosphorus in the same ratio of atoms as the ratio in aluminum phosphide.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Ga
• indium
• element 31
• element 49
Explain, in terms of electron configuration, why arsenic and antimony are chemically similar.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Arsenic atoms and antimony atoms each have 5 valence electrons.
• An As atom and a Sb atom both have five outermost electrons.
• same number of valence e−
A thiol is very similar to an alcohol, but a thiol has a sulfur atom instead of an oxygen atom in the functional group. The equation below represents a reaction of methanethiol and iodine, producing dimethyl disulfide and hydrogen iodide.
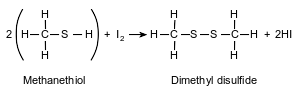
Explain, in terms of electron configuration, why sulfur atoms and oxygen atoms form compounds with similar molecular structures.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Sulfur and oxygen atoms both have 6 valence electrons.
• Atoms of both elements need the same number of electrons to complete their outer shells.
Before atomic numbers were known, Mendeleev developed a classification system for the 63 elements known in 1872, using oxide formulas and atomic masses. He used an R in the oxide formulas to represent any element in each group. The atomic mass was listed in parentheses after the symbol of each element. A modified version of Mendeleev’s classification system is shown in the table below.
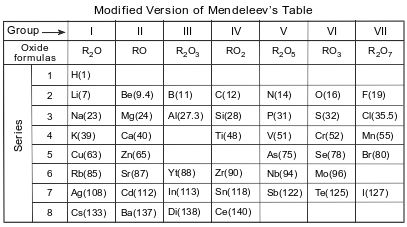
Based on Mendeleev’s oxide formula, what is the number of electrons lost by each atom of the elements in Group III?
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• three electrons
• three
• 3
Many scientists made observations of the elements that led to the modern Periodic Table. In 1829, Dobereiner found groups of three elements that have similar properties and called each of these groups a triad. Dobereiner noticed a relationship between the atomic masses of the elements in each triad. Triad 1, shown in the table below, consists of sulfur, selenium, and tellurium. The middle element, selenium, has an atomic mass that is close to the sum of the atomic masses of sulfur and tellurium, divided by 2.

The other triads shown in the table below demonstrate the same mathematical relationship.

Explain, in terms of electrons, why the elements in triad 2 have similar chemical properties.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• In the ground state, an atom of each of the elements has two valence electrons.
• An atom of each element has the same number of electrons in the outermost shell.
The elements in Group 2 on the Periodic Table can be compared in terms of first ionization energy, electronegativity, and other general properties.
Explain, in terms of electron configuration, why the elements in Group 2 have similar chemical properties.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The atoms in Group 2 elements have the same number of valence electrons and, therefore, similar chemical properties.
• Their atoms all have two valence electrons.
• Group 2 elements have 2 outermost electrons in each atom.
Explain, in terms of atomic structure, why Group 18 elements on the Periodic Table rarely form compounds.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Group 18 elements rarely form compounds because their atoms have stable electron configurations.
• Their valence shells are completely filled.
• All the elements have maximum numbers of valence electrons.
• Atoms of Group 18 have a stable octet except He, which is stable with two electrons.
