Topic: Proton Neutron Electron
Proton Neutron Electron
What is the number of electrons in an atom that has 3 protons and 4 neutrons?
(1) 1
(2) 7
(3) 3
(4) 4
An atom of lithium-7 has an equal number of
(1) electrons and neutrons
(2) electrons and protons
(3) positrons and neutrons
(4) positrons and protons
Which particle has no charge?
(1) electron
(2) neutron
(3) positron
(4) proton
What is the number of electrons in an Al3+ ion?
(1) 10
(2) 13
(3) 3
(4) 16
Which phrase describes the charge and mass of a neutron?
(1) a charge of +1 and no mass
(2) a charge of +1 and an approximate mass of 1 u
(3) no charge and no mass
(4) no charge and an approximate mass of 1 u
An ion that consists of 7 protons, 9 neutrons, and 10 electrons has a net charge of
(1) 2−
(2) 2+
(3) 3+
(4) 3−
What is the overall charge of an ion that has 12 protons, 10 electrons, and 14 neutrons?
(1) 2−
(2) 2+
(3) 4−
(4) 4+
Which statement describes the charge of an electron and the charge of a proton?
(1) An electron and a proton both have a charge of +1.
(2) An electron and a proton both have a charge of −1.
(3) An electron has a charge of +1, and a proton has a charge of −1.
(4) An electron has a charge of −1, and a proton has a charge of +1.
What is the number of electrons in an atom of scandium?
(1) 21
(2) 24
(3) 45
(4) 66
Which statement describes the charge and location of an electron in an atom?
(1) An electron has a positive charge and is located outside the nucleus.
(2) An electron has a positive charge and is located in the nucleus.
(3) An electron has a negative charge and is located outside the nucleus.
(4) An electron has a negative charge and is located in the nucleus.
The table below shows the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in four ions.
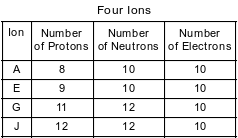
Which ion has a charge of 2−?
(1) A
(2) E
(3) G
(4) J
The diagram below represents a particle traveling through an electric field.
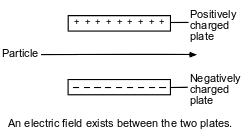
Which particle remains undeflected when passing through this electric field?
(1) proton
(2) electron
(3) neutron
(4) positron
Which subatomic particles are paired with their charges?
(1) electron–positive, neutron–negative, proton–neutral
(2) electron–negative, neutron–neutral, proton–positive
(3) electron–negative, neutron–positive, proton–neutral
(4) electron–neutral, neutron–positive, proton–negative
The atomic mass and natural abundance of the naturally occuring isotopes of hydrogen are shown in the table below.
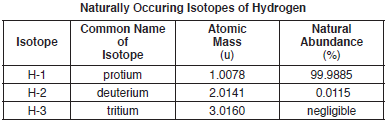
The isotope H-2, also called deuterium, is usually represented by the symbol “D.” Heavy water forms when deuterium reacts with oxygen, producing molecules of D2O.
Explain, in terms of subatomic particles, why atoms of H-1, H-2, and H-3 are each electrically neutral.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The single proton in each nucleus has a charge of +1. The single electron in each atom has a charge of −1. The net charge is 0.
• Each atom has one proton and one electron.
• Each atom has an equal number of protons and electrons.
• The total charge of the subatomic particles is zero.
The atomic radius and the ionic radius for some Group 1 and some Group 17 elements are given in the tables below.

Write both the name and the charge of the particle that is gained by an F atom when the atom becomes an F ion.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Particle: electron
• Charge of particle: −1
• Particle: electron
• Charge of particle: negative
