Topic: Rate Of A Chemical Reaction
Rate Of A Chemical Reaction
For a reaction at equilibrium, which change can increase the rates of the forward and reverse reactions?
(1) a decrease in the concentration of the reactants
(2) a decrease in the surface area of the products
(3) an increase in the temperature of the system
(4) an increase in the activation energy of the forward reaction
Which factors have the greatest effect on the rate of a chemical reaction between AgNO3(aq) and Cu(s)?
(1) solution concentration and temperature
(2) solution concentration and pressure
(3) molar mass and temperature
(4) molar mass and pressure
Given the balanced equation representing a reaction:
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + energy
Which change in reaction conditions will increase the frequency of effective collisions between reactant molecules?
(1) decreasing the pressure of the reactants
(2) decreasing the temperature of the reactants
(3) increasing the concentration of the reactants
(4) increasing the volume of the reactants
In the laboratory, a student investigates the effect of concentration on the reaction between HCl(aq) and Mg(s), changing only the concentration of HCl(aq). Data for two trials in the investigation are shown in the table below.
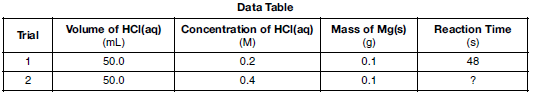
Compared to trial 1, what is the expected reaction time for trial 2 and the explanation for that result?
(1) less than 48 s, because there are fewer effective particle collisions per second
(2) less than 48 s, because there are more effective particle collisions per second
(3) more than 48 s, because there are fewer effective particle collisions per second
(4) more than 48 s, because there are more effective particle collisions per second
A 5.0-gram sample of Fe(s) is to be placed in 100. milliliters of HCl(aq). Which changes will result in the fastest rate of reaction?
(1) increasing the surface area of Fe(s) and increasing the concentration of HCl(aq)
(2) increasing the surface area of Fe(s) and decreasing the concentration of HCl(aq)
(3) decreasing the surface area of Fe(s) and increasing the concentration of HCl(aq)
(4) decreasing the surface area of Fe(s) and decreasing the concentration of HCl(aq)
Which sample of HCl(aq) reacts at the fastest rate with a 1.0-gram sample of iron filings?
(1) 10. mL of 1 M HCl(aq) at 10.°C
(2) 10. mL of 1 M HCl(aq) at 25°C
(3) 10. mL of 3 M HCl(aq) at 10.°C
(4) 10. mL of 3 M HCl(aq) at 25°C
Which statement explains why increasing the temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction, while other conditions remain the same?
(1) The reacting particles have less energy and collide less frequently.
(2) The reacting particles have less energy and collide more frequently.
(3) The reacting particles have more energy and collide less frequently.
(4) The reacting particles have more energy and collide more frequently.
As the temperature of a reaction increases, it is expected that the reacting particles collide
(1) more often and with greater force
(2) more often and with less force
(3) less often and with greater force
(4) less often and with less force
Several steps are involved in the industrial production of sulfuric acid. One step involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide gas to form sulfur trioxide gas. A catalyst is used to increase the rate of production of sulfur trioxide gas. In a rigid cylinder with a movable piston, this reaction reaches equilibrium, as represented by the equation below.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) + 392 kJ
Explain, in terms of collision theory, why increasing the pressure of the gases in the cylinder increases the rate of the forward reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• When the pressure in the cylinder is increased, the SO2(g) molecules and O2(g) molecules collide more frequently, producing more SO3(g).
The potential energy diagram and balanced equation shown below represent a reaction between solid carbon and hydrogen gas to produce 1 mole of C2H4(g) at 101.3 kPa and 298 K.

Identify one change in the reaction conditions, other than adding a catalyst, that can increase the rate of this reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Increase the temperature.
• Increase the pressure.
• Increase the concentration of H2(g).
• Increase the surface area of the carbon.
Carbon monoxide, CO(g), is a toxic gas found in automobile exhaust. The concentration of CO(g) can be decreased by using a catalyst in the reaction between CO(g) and O2(g). This reaction is represented by the balanced equation below.

Explain, in terms of collision theory, why an increase in temperature increases the rate of the reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The rate of the chemical reaction increases because the reactant molecules move faster and collide with more kinetic energy.
• Increasing the temperature causes more frequent collisions.
• As molecules acquire more kinetic energy, the probability of effective collisions increases.
• More reactant molecules collide with sufficient energy.
The balanced equation below represents the reaction between a 5.0-gram sample of zinc metal and a 0.5 M solution of hydrochloric acid. The reaction takes place in an open test tube at 298 K and 1 atm in a laboratory activity.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) + energy
State one change in reaction conditions, other than adding a catalyst, that will increase the rate of the reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Increase the surface area of the zinc.
• Increase the temperature of the reaction.
• Use a more concentrated HCl(aq) solution.
Calcium reacts with water. This reaction is represented by the balanced equation below. The aqueous product of this reaction can be heated to evaporate the water, leaving a white solid, Ca(OH)2(s).
Ca(s) + 2H2O(ℓ) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
State one change in reaction conditions that will increase the rate of the reaction.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Increase the temperature of the water.
• Increase the surface area of Ca(s).
In a laboratory apparatus, a sample of lead(II) oxide reacts with hydrogen gas at high temperature. The products of this reaction are liquid lead and water vapor. As the reaction proceeds, water vapor and excess hydrogen gas leave the glass tube. The diagram and balanced equation below represent this reaction.
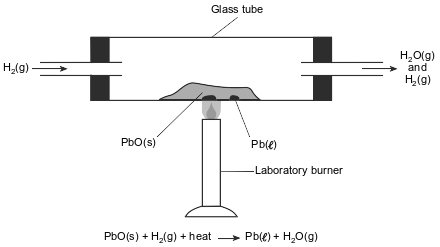
State one change in reaction conditions, other than adding a catalyst, that would cause the rate of this reaction to increase.
Methanol can be manufactured by a reaction that is reversible. In the reaction, carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas react using a catalyst. The equation below represents this system at equilibrium.
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g) + energy
Explain, in terms of collision theory, why increasing the concentration of H2(g) in this system will increase the concentration of CH3OH(g).
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• More H2(g) molecules collide with CO(g) molecules, producing more CH3OH(g).
• Adding H2 increases the number of effective collisions to produce more methanol.
• A greater number of effective collisions occur.
