Topic: Solutions
Solutions
A solution consists of 0.50 mole of CaCl2 dissolved in 100. grams of H2O at 25°C. Compared to the boiling point and freezing point of 100. grams of H2O at standard pressure, the solution at standard pressure has
(1) a lower boiling point and a lower freezing point
(2) a lower boiling point and a higher freezing point
(3) a higher boiling point and a lower freezing point
(4) a higher boiling point and a higher freezing point
Which compound is soluble in water?
(1) PbS
(2) BaS
(3) Na2S
(4) Fe2S3
According to Table F, which ions combine with chloride ions to form an insoluble compound?
(1) Fe2+ ions
(2) Ca2+ ions
(3) Li+ ions
(4) Ag+ ions
Which sample, when dissolved in 1.0 liter of water, produces a solution with the highest boiling point?
(1) 0.1 mole KI
(2) 0.2 mole KI
(3) 0.1 mole MgCl2
(4) 0.2 mole MgCl2
Based on Table F, which compound is least soluble in water?
(1) AlPO4
(2) Li2SO4
(3) Ca(OH)2
(4) AgC2H3O2
Based on Table F, which equation represents a saturated solution having the lowest concentration of Cl− ions?
(1) NaCl(s) ⇌ Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
(2) AgCl(s) ⇌ Ag+(aq) + Cl−(aq) +(aq) + Cl−(aq)
(3) NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH4
(4) KCl(s) ⇌ K+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
Ammonium chloride is dissolved in water to form a 0.10 M NH4Cl(aq) solution. This dissolving process is represented by the equation below.

Determine the minimum mass of NH4Cl(s) required to produce a saturated solution in 100. grams of water at 40.°C.
Allow 1 credit for 47 g ± 1 g.
The compounds KNO3 and NaNO3 are soluble in water.
Compare the boiling point of a NaNO3 solution at standard pressure to the boiling point of water at standard pressure.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The boiling point of the NaNO3 solution is higher than the boiling point of water.
• lower for H2O
Baking soda, NaHCO3, can be commercially produced during a series of chemical reactions called the Solvay process. In this process, NH3(aq), NaCl(aq), and other chemicals are used to produce NaHCO3(s) and NH4Cl(aq).
To reduce production costs, NH3(aq) is recovered from NH4Cl(aq) through a different series of reactions. This series of reactions can be summarized by the overall reaction represented by the unbalanced equation below.
NH4Cl(aq) + CaO(s) → NH3(aq) + H2O(ℓ) + CaCl2(aq)
Determine the mass of NH4Cl that must be dissolved in 100. grams of H2O to produce a saturated solution at 70.°C.
Allow 1 credit for any value from 61 g to 63 g, inclusive.
The formulas and the boiling points at standard pressure for ethane, methane, methanol, and water are shown in the table below.

Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why the solubility of methanol in water is greater than the solubility of methane in water.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Methanol and water molecules are polar, but methane molecules are nonpolar.
• The compounds methanol and water have similar polarities.
Seawater contains dissolved salts in the form of ions. Some of the ions found in seawater are Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, Cl−, HCO3−, and SO42−. An investigation was conducted to determine the concentration of dissolved salts in seawater at one location. A 300.-gram sample of the seawater was placed in an open container. After a week, all the water had evaporated and 10. grams of solid salts remained in the container.
At standard pressure, compare the freezing point of seawater to the freezing point of distilled water.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Water has a higher freezing point than seawater.
• Seawater’s is lower.
A student prepares two 141-gram mixtures, A and B. Each mixture consists of NH4Cl, sand, and H2O at 15°C. Both mixtures are thoroughly stirred and allowed to stand. The mass of each component used to make the mixtures is listed in the data table below.
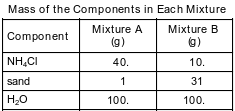
Determine the temperature at which all of the NH4Cl in mixture A dissolves to form a saturated solution.
Allow 1 credit for any value from 23ºC to 26ºC, inclusive.
A solution of ethylene glycol and water can be used as the coolant in an engine-cooling system. The ethylene glycol concentration in a coolant solution is often given as percent by volume. For example, 100. mL of a coolant solution that is 40.% ethylene glycol by volume contains 40. mL of ethylene glycol diluted with enough water to produce a total volume of 100. mL. The graph below shows the freezing point of coolants that have different ethylene glycol concentrations.
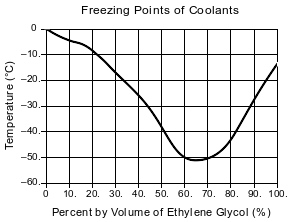
Explain, in terms of the molecular polarity, why ethylene glycol dissolves in water to form a solution.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable response include, but are not limited to:
• Water molecules and ethylene glycol molecules are both polar.
• Water and the glycol have similar polarities.
In a laboratory investigation, a student is given a sample that is a mixture of 3.0 grams of NaCl(s) and 4.0 grams of sand, which is mostly SiO2(s). The purpose of the investigation is to separate and recover the compounds in the sample. In the first step, the student places the sample in a 250-mL flask. Then, 50. grams of distilled water are added to the flask, and the contents are thoroughly stirred. The mixture in the flask is then filtered, using the equipment represented by the diagram below.
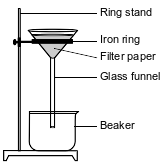
Explain, in terms of solubility, why the mixture in the flask remains heterogeneous even after thorough stirring.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The NaCl(s) dissolves in H2O(ℓ), but sand does not dissolve.
• The sand is insoluble in water.
• After the stirring, the sand settles to the bottom of the flask.
What is the mass of KNO3(s) that must dissolve in 100. grams of water to form a saturated solution at 50.°C?
Allow 1 credit for 84 g ± 2 g.
