Topic: Table O Symbols Used In Nuclear Chemistry
Table O Symbols Used In Nuclear Chemistry
Which particles have approximately the same mass?
(1) alpha particle and beta particle
(2) alpha particle and proton
(3) neutron and positron
(4) neutron and proton
Nuclei of U-238 atoms are
(1) stable and spontaneously absorb alpha particles
(2) stable and spontaneously emit alpha particles
(3) unstable and spontaneously absorb alpha particles
(4) unstable and spontaneously emit alpha particles
Which nuclear emission has the greatest penetrating power?
(1) proton
(2) beta particle
(3) gamma radiation
(4) positron
Which particle has no charge?
(1) electron
(2) neutron
(3) positron
(4) proton
Which statement describes the relative masses of two different particles?
(1) A neutron has less mass than a positron.
(2) A beta particle has less mass than a neutron.
(3) An alpha particle has less mass than a positron.
(4) An alpha particle has less mass than a beta particle.
Which phrase describes the charge and mass of a neutron?
(1) a charge of +1 and no mass
(2) a charge of +1 and an approximate mass of 1 u
(3) no charge and no mass
(4) no charge and an approximate mass of 1 u
Which nuclear emission is negatively charged?
(1) an alpha particle
(2) a beta particle
(3) a neutron
(4) a positron
Compared to an electron, which particle has a charge that is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign?
(1) an alpha particle
(2) a beta particle
(3) a neutron
(4) a proton
Which list of nuclear emissions is arranged in order from the greatest penetrating power to the least penetrating power?
(1) alpha particle, beta particle, gamma ray
(2) alpha particle, gamma ray, beta particle
(3) gamma ray, alpha particle, beta particle
(4) gamma ray, beta particle, alpha particle
Which particle has the least mass?
(1) a proton
(2) an electron
(3) a helium atom
(4) a hydrogen atom
Which particle has the least mass?
(1) alpha particle
(2) beta particle
(3) neutron
(4) proton
A student compares some models of the atom. These models are listed in the table below in order of development from top to bottom.
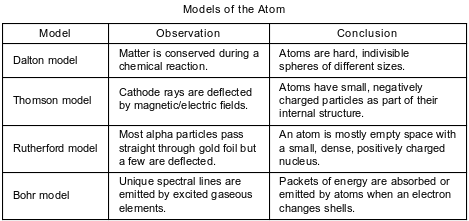
Using the conclusion from the Rutherford model, identify the charged subatomic particle that is located in the nucleus.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• proton
• p
• p+
• 11p
• 11H
• H+
Cobalt-60 is an artificial isotope of Co-59. The incomplete equation for the decay of cobalt-60, including beta and gamma emissions, is shown below.

Compare the penetrating power of the beta and gamma emissions.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The gamma radiation has more penetrating power than the beta emission.
• The β− is less penetrating than γ.
• Gamma emissions have greater penetrating power.
In the past, some paints that glowed in the dark contained zinc sulfide and salts of Ra-226. As the radioisotope Ra-226 decayed, the energy released caused the zinc sulfide in these paints to emit light. The half-lives for Ra-226 and two other radioisotopes used in these paints are listed on the table below.

Complete the nuclear equation below for the beta decay of Pm-147 by writing an isotopic notation for the missing product.
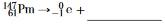
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• 14762Sm
• Sm-147
• 147Sm
• samarium-147
Illuminated EXIT signs are used in public buildings such as schools. If the word EXIT is green, the sign may contain the radioisotope tritium, hydrogen-3. The tritium is a gas sealed in glass tubes. The emissions from the decay of the tritium gas cause a coating on the inside of the tubes to glow.
Complete the nuclear equation below for the radioactive decay of tritium, by writing a notation for the missing product.
gralphfile:chem62014-abkq85.png
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• 32He
• helium-3
• He-3
• 3He
