Topic: Table Q Homologous Series Of Hydrocarbons
Table Q Homologous Series Of Hydrocarbons
Which formula represents an organic compound?
(1) CaH2
(2) C4H8
(3) H2O2
(4) P2O5
Which compound is classified as a hydrocarbon?
(1) butanal
(2) butyne
(3) 2-butanol
(4) 2-butanone
Which condensed structural formula represents an unsaturated compound?
(1) CH3CHCHCH3
(2) CH3CH2CH3
(3) CH3CH3
(4) CH4
Which formula represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
(1) C2H4
(2) C3H8
(3) C4H10
(4) C5H12
Which formula represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
(1) CH4
(2) C2H4
(3) C3H8
(4) C4H10
Given the formula representing a compound:

What is a chemical name of this compound?
(1) 2-pentene
(2) 2-pentyne
(3) 3-pentene
(4) 3-pentyne
Hydrocarbons are composed of the elements
(1) carbon and hydrogen, only
(2) carbon and oxygen, only
(3) carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
(4) carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen
What is the name of the compound with the formula CH3CH2CH2NH2?
(1) 1-propanol
(2) 1-propanamine
(3) propanal
(4) propanamide
A molecule of any organic compound has at least one
(1) ionic bond
(2) double bond
(3) oxygen atom
(4) carbon atom
The equation below represents the reaction between 1-butene and bromine to form the compound 1,2-dibromobutane, C4H8Br2.

Explain, in terms of bonding, why the hydrocarbon reactant is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Each reactant hydrocarbon molecule has a double carbon-carbon bond.
• There is a multiple carbon-carbon bond in each molecule.
• More hydrogen atoms can be bonded with this hydrocarbon.
Natural gas and coal are two fuels burned to produce energy. Natural gas consists of approximately 80% methane, 10% ethane, 4% propane, 2% butane, and other components.
The burning of coal usually produces sulfur dioxide, SO2(g), and sulfur trioxide, SO3(g), which are major air pollutants. Both SO2(g) and SO3(g) react with water in the air to form acids.
Write the general formula for the homologous series that includes the components of the natural gas listed in this passage.
Allow 1 credit for CnH2n+2.
Crude oil, primarily a mixture of hydrocarbons, is separated into useful components in a fractionating tower. At the bottom of the tower, the crude oil is heated to about 400°C. The gases formed rise and cool. Most of the gases condense and are collected as liquid fractions. The table below shows the temperature ranges for collecting various hydrocarbon fractions.
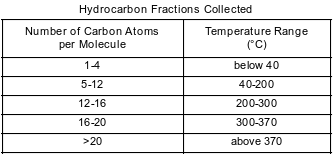
Determine the number of carbon atoms in one molecule of an alkane that has 22 hydrogen atoms in the molecule.
Allow 1 credit for 10 or ten.
The formulas for two compounds are shown below.

Explain, in terms of bonding, why compound A is saturated.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• All the carbon-to-carbon bonds are single bonds.
• The maximum number of H atoms are bonded to the carbon chain.
• There are no multiple bonds.
- A test tube contains a sample of solid stearic acid, an organic acid.
- Both the sample and the test tube have a temperature of 22.0°C.
- The stearic acid melts after the test tube is placed in a beaker with 320. grams of water at 98.0°C.
- The temperature of the liquid stearic acid and water in the beaker reaches 74.0°C.
Identify the element in stearic acid that makes it an organic compound.
Allow 1 credit for C or carbon.
Fruit growers in Florida protect oranges when the temperature is near freezing by spraying water on them. It is the freezing of the water that protects the oranges from frost damage. When H2O(ℓ) at 0°C changes to H2O(s) at 0°C, heat energy is released. This energy helps to prevent the temperature inside the orange from dropping below freezing, which could damage the fruit. After harvesting, oranges can be exposed to ethene gas, C2H4, to improve their color.
Write the empirical formula for ethene.
Allow 1 credit for CH2. The order of the elements may vary.
