Topic: Table S Properties Of Selected Elements
Table S Properties Of Selected Elements
Compared to a 1.0-gram sample of chlorine gas at standard pressure, a 1.0-gram sample of solid aluminum at standard pressure has
(1) a lower melting point
(2) a higher boiling point
(3) a lower density
(4) a greater volume
In the ground state, an atom of each of the elements in Group 2 has a different
(1) oxidation state
(2) first ionization energy
(3) number of valence electrons
(4) number of electrons in the first shell
At 298 K and 1 atm, which noble gas has the lowest density?
(1) Ne
(2) Kr
(3) Xe
(4) Rn
Which general trend is found in Period 3 as the elements are considered in order of increasing atomic number?
(1) increasing atomic radius
(2) increasing electronegativity
(3) decreasing atomic mass
(4) decreasing first ionization energy
Which statement describes the general trends in electronegativity and first ionization energy as the elements in Period 3 are considered in order from Na to Cl?
(1) Electronegativity increases, and first ionization energy decreases.
(2) Electronegativity decreases, and first ionization energy increases.
(3) Electronegativity and first ionization energy both increase.
(4) Electronegativity and first ionization energy both decrease.
Which property decreases when the elements in Group 17 are considered in order of increasing atomic number?
(1) atomic mass
(2) atomic radius
(3) melting point
(4) electronegativity
Which element has a melting point higher than the melting point of rhenium?
(1) iridium
(2) osmium
(3) tantalum
(4) tungsten
Which list of elements is arranged in order of increasing electronegativity?
(1) Be, Mg, Ca
(2) F, Cl, Br
(3) K, Ca, Sc
(4) Li, Na, K
Which element is a liquid at 1000. K?
(1) Ag
(2) Al
(3) Ca
(4) Ni
The atomic number and corresponding atomic radius of the Period 3 elements are shown in the data table below.
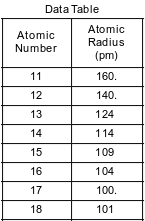
State the general relationship between the atomic number and the atomic radius for the Period 3 elements.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As atomic number increases, there is a decrease in atomic radius.
The diagram below represents three elements in Group 13 and three elements in Period 3 and their relative positions on the Periodic Table.
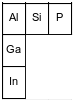
Some elements in the solid phase exist in different forms that vary in their physical properties. For example, at room temperature, red phosphorus has a density of 2.16 g/cm3 and white phosphorus has a density of 1.823 g/cm3.
Consider the Period 3 elements in the diagram in order of increasing atomic number. State the trend in electronegativity for these elements.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As atomic number increases, the electronegativity increases.
• Electronegativity increases.
• from lower to higher
Periodic trends are observed in the properties of the elements in Period 3 on the Periodic Table. These elements vary in physical properties, such as phase, and in chemical properties, such as their ability to lose or gain electrons during a chemical reaction.
Identify the element in Period 3 that requires the least amount of energy to remove the most loosely held electrons from a mole of gaseous atoms of the element in the ground state.
Allow 1 credit for Na or sodium.
The elements in Group 17 are called halogens. The word “halogen” is derived from Greek and means “salt former.”
State the trend in electronegativity for the halogens as these elements are considered in order of increasing atomic number.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• As atomic number increases, electronegativity decreases.
• Electronegativity decreases.
A technician recorded data for two properties of Period 3 elements. The data are shown in the table below.
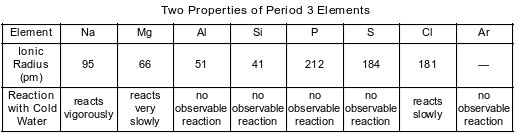
State the phase of chlorine at 281 K and 101.3 kPa.
Allow 1 credit for gas or (g).
State the general trend in first ionization energy as the elements in Period 3 are considered from left to right.
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• The first ionization energies of the elements in Period 3 generally increase from left to right.
• Ionization energy increases.
