Topic: Erosion And Natural Agents Of Erosion
Erosion And Natural Agents Of Erosion
A mudslide is most likely to occur on a hillslope having soil that is
(1) saturated with water and without vegetation
(2) saturated with water and covered by vegetation
(3) unsaturated and without vegetation
(4) unsaturated and covered by vegetation
The map below shows coastal features of a portion of Long Island, New York. Point A represents a location on a landscape feature that resulted from wave action and longshore currents.
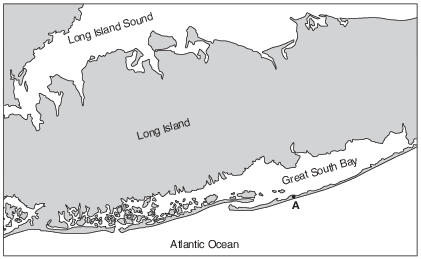
On which landscape feature is point A located?
(1) moraine
(2) delta
(3) barrier island
(4) floodplain
Sandstone, limestone, and conglomerate cobbles are found in a streambed in New York State where the surrounding bedrock is composed of shales and siltstones. The most likely explanation for the presence of these cobbles is that they were
(1) weathered from the surrounding bedrock
(2) formed when shale and siltstone bedrock were eroded
(3) transported to this area from another region
(4) metamorphosed from shale and siltstone
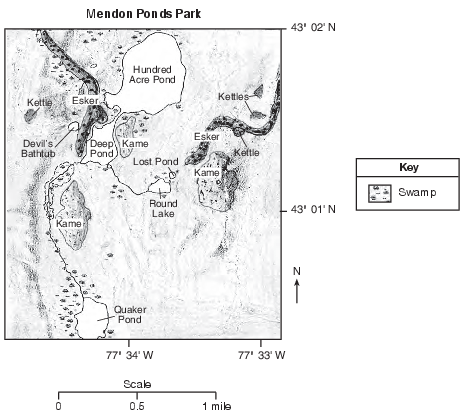
Mendon Ponds Park
Mendon Ponds Park, in New York State, is listed in the National Registry of National Landmarks due to its outstanding glacial landscape features. Glacial ice that covered most of New York State retreated northward at the end of the last ice age. As this glacial ice melted, great amounts of sediments were deposited at the glacier’s southern edge. Four glacial features dominate the park’s landscape. Kettles are bowl-shaped depressions formed when buried blocks of glacial ice melt. If the depressions fill with water, they are called kettle lakes. The Mendon Park ponds are all kettle lakes. Eskers are ridges of sorted sediments deposited within streams flowing beneath the melting glacier. Kames are small hills of unsorted sediment deposited at the base of waterfalls formed by streams flowing over the edge of a melting glacier.
The cross sections below represent how a present-day glacial landscape feature was formed in Mendon Ponds Park and its appearance at present.
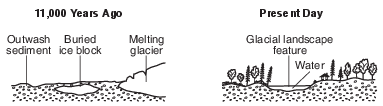
Which glacial landscape feature is indicated in the present-day cross section?
(1) esker
(2) kame
(3) finger lake
(4) kettle lake
Crete Earthquake
Scientists have located the geological fault, off the coast of Crete in the Mediterranean Sea, that likely shifted, causing a huge earthquake in the year 365 that devastated life and property on Crete. The southwestern coastal region of Crete was uplifted, as evidenced by remains of corals and other sea life now found on land 10 meters above sea level. Scientists measured the age of these corals to verify when this event occurred. This earthquake caused a tsunami that devastated the southern and eastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. It is estimated that earthquakes along the fault, associated with the Hellenic Trench, may occur about every 800 years.

Which activity could best prepare residents along the Mediterranean coast to reduce the loss of human life during a future tsunami?
(1) Board up windows.
(2) Remove heavy objects from the walls in homes.
(3) Plan evacuation routes to higher ground.
(4) Build reinforced basements.
Bedrock layers

The landscape feature labeled X is best described as
(1) a flood plain
(2) a sand bar
(3) a delta
(4) an escarpment
The photograph below shows wire netting installed over a steep rock outcrop.

This wire netting has been installed to prevent loss of property or life resulting from
(1) crosscutting and downwarping
(2) folding and faulting
(3) weathering and erosion
(4) high winds and flooding
Which New York State river generally fl ows southward?
(1) Genesee
(2) Hudson
(3) Niagara
(4) St. Lawrence
The surface bedrock in the Hudson Highlands consists mostly of
(1) diabase, dolostone, and granite
(2) slate, siltstone, and basalt
(3) gneiss, quartzite, and marble
(4) limestone, shale, sandstone, and conglomerate
The diagram below represents three identical beakers, A, B, and C, each containing an equal volume of uniform-sized spherical beads. Water is poured into each beaker until all of the pore spaces are filled.

Which table best indicates the percentage of pore space compared to the total volume of each beaker?
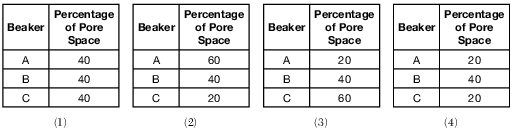
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
Huygens Probe Lands on Titan
The Huygens probe was carried to Saturn by the Cassini spacecraft and parachuted to the surface of Saturn’s giant moon, Titan. The Huygens probe’s landing site was littered with smooth, rounded, rocklike objects. Photographs taken of Titan’s surface show drainage channels leading to an apparent shoreline. The question is, what are they draining? One of the photographs seems to show ground fog consisting not of water, but perhaps of ethane or methane.

What natural process occurring on Earth produces smooth, rounded rocks similar to those found at the probe’s landing site on Titan? [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — weathering and/or erosion
• — rock abrasion
• — transport by running water
• — wave action

State one reason for the restriction of the construction of buildings near a meandering river on a coastal plain. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Buildings could be damaged or destroyed by flooding.
• — The river’s course changes due to erosion and deposition.
• — It’s on the floodplain.
• — The ground might be unstable.
• — The ground can become saturated/a swamp.
• — The meanders change positions over time.
Devastating Tsunami
On March 11, 2011, one of the largest earthquakes ever recorded (magnitude 9.0) produced a 7-meter-high tsunami that devastated Japan’s eastern coast. Thousands of people died and billions of dollars in damage occurred. Several hours after the earthquake, the tsunami reached the Hawaiian Islands and parts of North America’s west coast.

Describe one immediate action that was most likely taken in the Hawaiian Islands to prevent the loss of life as the tsunami approached. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Sound alarm for residents.
• — Move to higher ground.
• — Evacuate coastal areas.
• — Broadcast radio/TV bulletins.
• — Move ships away from the coast.
• — Follow evacuation routes.

A 25-foot high tsunami hit the Japanese city of Ishinomaki. Describe a precaution the city could take now to protect citizens from tsunamis in future years. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — install a tsunami monitoring and warning system
• — build a seawall/barricade/barrier
• — build tall structures on stronger foundations
• — designate or plan evacuation routes
• — prepare emergency kits/supplies
• — relocate buildings to higher ground
• Note: Do not allow credit for an action indicating an imminent tsunami (e.g., evacuate to higher
• ground).
Meteorite Composition
Meteors that strike Earth’s surface are called meteorites. Analysis of meteorite composition has provided scientists with information regarding the formation of Earth and our solar system, and possibly the development and evolution of life on Earth.
Two types of meteorites are iron meteorites and chondrites. Iron meteorites consist mostly of iron and nickel, and are inferred to be from core materials of early planetary bodies in our solar system. More than 60% of meteorites studied have been identified as chondrites. Chondrites are made of millimeter-sized spheres of olivine and pyroxene crystals embedded in a mass of mineral and metal grains. The chondrites are thought to represent fragments of the earliest solid materials in our solar system. One type of chondrite, the carbonaceous chondrite, contains water, organic compounds, and minerals that represent the chemical composition necessary for life to form.
Explain why there is little evidence of meteorite impact craters on Earth. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Weathering and erosion on Earth’s surface have erased many craters.
• — Most meteors are very small and burn up in Earth’s atmosphere.
• — Most of Earth’s surface is ocean, where sediments cover impact craters.
• — Crustal plate movement has destroyed the evidence.
