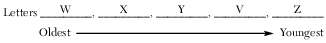Topic: Relative Age And Sequence Of Rock Strata
Relative Age And Sequence Of Rock Strata
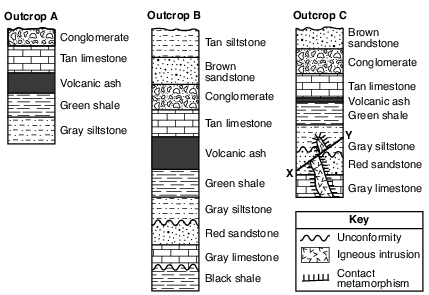
What is the youngest sedimentary rock layer represented in these cross sections?
(1) black shale
(2) brown sandstone
(3) tan siltstone
(4) conglomerate
The geologic cross section below shows bedrock layers A through D. Line XY is a fault.
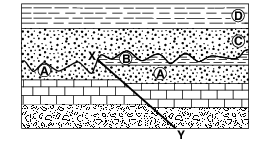
The fault most likely occurred after
(1) all bedrock layers were formed
(2) layer C formed, but before layer D formed
(3) layer A formed, but before layer B formed
(4) layer B formed, but before layer C formed
Which index fossil has been found in Ordovician-age bedrock?

(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4

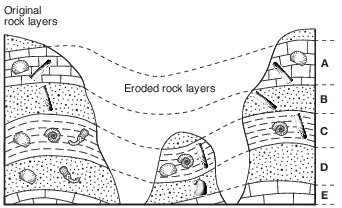
Which sequence best describes the geologic history, from oldest to youngest, that occurred at this site?
(1) deposition of F, D, C, B → intrusion of E → uplift and erosion → deposition of A
(2) intrusion of E → deposition of F, D, C, B → uplift and erosion → deposition of A
(3) deposition of F, D, C, B, A → uplift and erosion → intrusion of E
(4) deposition of F, D, C, B, A → intrusion of E → uplift and erosion
Valcouroceras is a New York State index fossil. Which mountain-building event occurred in New York State during the time when Valcouroceras was living in oceans covering parts of New York State?
(1) Alleghenian orogeny
(2) Acadian orogeny
(3) Taconian orogeny
(4) Grenville orogeny
The diagram below represents three bedrock outcrops. The layers have not been overturned. Letters A through E identify different rock layers. Fossils found in the rock layers are shown.
Which fossil could be classified as an index fossil?

(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
The geologic cross section below includes an unconformity and an igneous intrusion.

Which two events produced the geologic unconformity in the rock record?
(1) intrusion of magma, followed by contact metamorphism
(2) intrusion of magma, followed by erosion of rock layers
(3) erosion of rock layers, followed by deposition of more sediments
(4) erosion of rock layers, followed by intrusion of magma
The cross sections below represent three outcrops, labeled I, II, and III, containing some New York State index fossils. The rock layers have not been overturned.
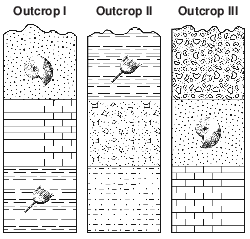
When the rock layers in the three outcrops are correlated, the oldest layer is the
(1) shale layer in outcrop I
(2) siltstone layer in outcrop II
(3) limestone layer in outcrop III
(4) conglomerate layer in outcrop III
The bedrock cross section below contains rock formations A, B, C, and D. The rock formations have not been overturned.

Which sequence represents the relative ages of these rock formations, from oldest to youngest?
(1) B → A → C → D
(2) B → D → C → A
(3) D → C → A → B
(4) D → B → A → C
Frozen Mammoth
A wooly mammoth was found in 1999 buried in the frozen soil of the Siberian tundra. Carbon-14 dating indicated that it had died about 20,000 years ago. Many fossils represent only the partial remains of organisms. However, a complete mammoth with bones, skin, hair, and internal organs intact represented a unique opportunity for scientists to investigate the lifestyle of this animal and the environment in which it lived.
Identify one New York State index fossil of an organism that lived during the same time as the wooly mammoth. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — mastodont
• — beluga whale
• — condor
• — humans
The Great Rift Valley
Rifting of Earth’s crust in eastern Africa began during the Neogene Period as the Ethiopian and Kenyan Domes formed. These two huge domes were created as Earth’s mantle pushed up the overlying crust. As the crust was forced upward, the resulting tension cracked the crust, resulting in the eruption of volcanoes and the formation of large rifts. The crust continued to pull apart, forming rift valleys. These valleys have become deeper and are currently becoming filled with sediments, igneous rock, and water.
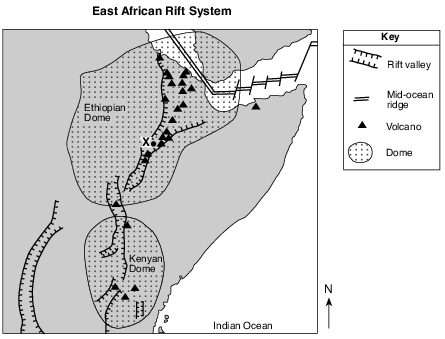
How many million years ago did the Ethiopian and Kenyan Domes form? [1]
million years ago
Allow 1 credit for any value from 23 million years ago to 1.8 million years ago.
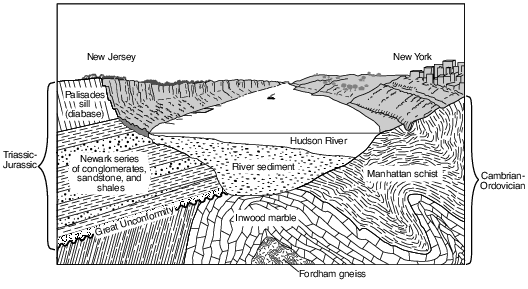
Identify the oldest bedrock shown in the diagram. [1]
Allow 1 credit for Fordham gneiss or gneiss.



Identify the New York State index fossil group that includes fossil 4 shown on the rock sample. [1]
Allow 1 credit for brachiopods or Mucrospirifer.
Indicate the relative ages of geologic features B, E, F, and X, by listing the letters from oldest to most recent. [1]

Allow 1 credit for the sequence shown below.
• 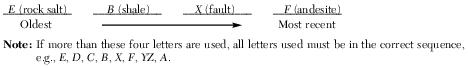
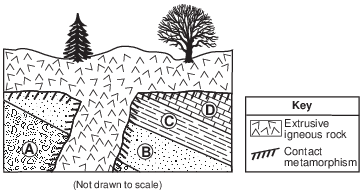
Geologic events V through Z are listed below.
V. Metamorphism of some sedimentary rock
W. Formation of sedimentary rock layers
X. Tilting and erosion of sedimentary rock layers
Y. Intrusion/extrusion of igneous rock
Z. Erosion of some igneous rock
List the letters V through Z to indicate the correct order of the geologic events, from oldest to youngest, that formed this portion of Earth’s crust. [1]

Allow 1 credit for the sequence shown below:
•