Topic: Energy Flow And Food Web
Energy Flow And Food Web
The diagram below represents a food web in a pond ecosystem.

Two carnivores in the food web are
(1) bass and small invertebrates
(2) small invertebrates and crabs
(3) water plants and clams
(4) crabs and crayfish
Many families now use compost to make the soil in their gardens more fertile. They collect vegetable scraps and yard trimmings, place them in a compost pile or special container, and let them decompose. The organisms primarily responsible for decomposing the vegetable scraps and yard trimmings are
(1) plant parasites
(2) autotrophs
(3) bacteria and fungi
(4) scavengers and viruses
A food chain is represented below.
grass → rabbit → hawk
Structures within the rabbit are formed using
(1) solar energy from the grass
(2) heat energy lost to the environment
(3) chemical energy from the hawk
(4) chemical energy from the grass
Which sequence best represents the flow of energy through an ecosystem?
(1) Sun → green plants → herbivores → carnivores
(2) Sun → herbivores → producers → consumers
(3) green plants → carnivores → consumers → herbivores
(4) consumers → carnivores → herbivores → producers
A food web is represented below.
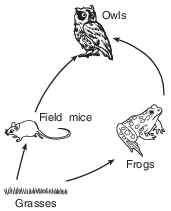
Which organism would receive the least amount of transferred solar energy?
(1) grasses
(2) owls
(3) frogs
(4) field mice
The sequence that best illustrates the flow of energy through an ecosystem is
(1) sunlight → plant → wolf → rabbit
(2) plant → sunlight → rabbit → wolf
(3) sunlight → plant → rabbit → wolf
(4) wolf → rabbit → plant → sunlight
The diagram below represents relationships in an ecosystem.

What is the primary source of energy in this environment?
(1) cellular respiration in the plants
(2) energy from minerals in the soil
(3) fossil fuels
(4) solar energy

The organisms found at the second trophic level of this pyramid would be
(1) producers
(2) decomposers
(3) carnivores
(4) herbivores
The final consumers in many food webs are
(1) autotrophs
(2) hosts
(3) herbivores
(4) carnivores

Energy in this ecosystem passes directly from the Sun to
(1) herbivores
(2) consumers
(3) heterotrophs
(4) autotrophs
Which statement describes an activity of a decomposer?
(1) A mushroom digests and absorbs nutrients from organic matter.
(2) A sunflower uses nutrients from the soil to make proteins.
(3) A snail scrapes algae off rocks in an aquarium.
(4) A hawk eats and digests a mouse.
Species A, B, C, and D are all different heterotrophs involved in the same food chain in an ecosystem. The table below shows the population of each of these species on one summer day.
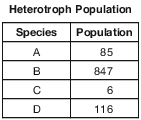
Which species is most likely an herbivore? Support your answer with data from the table. [1]
Species: ________________________________________
Allow 1 credit for B and supporting the answer. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — In a food pyramid, the largest population of heterotrophs would be the herbivores and B is
• the largest group.
• — Most animals in an ecosystem are herbivores.
• — In most ecosystems, herbivores outnumber other heterotrophs.
Gray Wolves in the Rocky Mountains
Reintroduction of gray wolves in the northern Rocky Mountains has increased the ecological health of Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming. When all wolves in Yellowstone National Park were killed in 1920, elk soon ate trees and shrubs down to short stubs. Now that wolves are reducing elk numbers, many aspens and willow trees are taller and fuller and birds are returning to the trees to nest. The beaver population has grown from one colony to 12 colonies in 13 years. Spreading these benefits across the Rocky Mountain region would require increasing the present wolf population of 1,770 to 17,000.
In September 2012, wolves lost federal protection in Wyoming. In 2014, Wyoming closed its hunting season after meeting its quota of 26 wolves around Yellowstone and Grand Teton parks. The sizes of traps to catch wolves have been regulated to reduce the chance of trapping endangered species such as lynx and wolverines and the hunting season was shortened. Some ecologists wonder if removing the wolves from federal protection and allowing them to be hunted is a good ecological decision.
In the space below, construct a food chain using three organisms identified in the above passage. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — trees → elk → wolves
• — willows → beavers → wolves
• — aspens → elk → wolves
• — shrubs → elk → humans
• — trees → beavers → lynx
• Note: Do not deduct credit if the Sun is included with the three organisms.

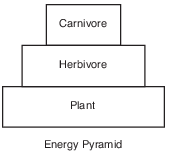
Complete the energy pyramid provided below by writing herbivore, plant, and carnivore in the correct locations. [1]

Energy Pyramid
Allow 1 credit for:
• 

Identify which group of organisms in this food web would contain the greatest amount of stored energy. Support your answer. [1]
Organisms:
Support:
Allow 1 credit for identifying which group of organisms in this food web would contain the great-
• est amount of stored energy and supporting the answer. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The greatest amount of stored energy in this food web would be in the plants because they
• obtain energy directly from the Sun.
• — Plants would, since they are the producers/autotrophs.
• — Plants, seeds, needles, and leaf litter would have the most energy because they are at the
• base of the energy pyramid/beginning of food chains.
