Topic: Levels Of Organization For Structure And Function
Levels Of Organization For Structure And Function
Prions are proteins that act as an infectious agent. They cause a variety of diseases, including “Mad Cow” disease. Prions cannot produce more prions on their own, but cause the host organism to replicate more prions. Most scientists do not consider prions to be alive. A valid reason for accepting that prions are nonliving things is that
(1) no living thing can cause a disease
(2) proteins are inorganic molecules
(3) prions contain all of the material needed to reproduce
(4) prions cannot carry out reproduction independently
The diagram below represents an incomplete sequence of levels of organization.
organelles → tissues → organs → organ systems → organism
This sequence can be completed correctly by inserting
(1) “cells →” between organelles and tissues
(2) “proteins →” between tissues and organs
(3) “populations →” between organs and organ systems
(4) “molecules →” between organ systems and organisms
Which sequence best represents increasing complexity?
(1) tissues → cells → organelles → organs
(2) cells → organelles → organs → organism
(3) organelles → cells → tissues → organs
(4) organism → cells → tissues → organelles
Rabbits have evolved strategies that get them through periods of time when there is little food. The diagram below represents essential life functions that rabbits need to perform.
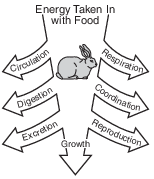
Which life function in the diagram could be eliminated without affecting an individual rabbit’s ability to survive when food is scarce?
(1) digestion
(2) excretion
(3) circulation
(4) reproduction
Bacteria and humans are similar in that they both
(1) contain genetic material
(2) are single-celled
(3) lack cell organelles
(4) carry out autotrophic nutrition
During gas exchange, the cell membrane of a single-celled organism has the same function as which organ system in humans?
(1) nervous
(2) reproductive
(3) digestive
(4) respiratory
Which sequence represents structures organized from least complex to most complex?
(1) nerve cell → nucleus → nervous system → brain
(2) nucleus → nerve cell → brain → nervous system
(3) brain → nervous system → nucleus → nerve cell
(4) nervous system → brain → nerve cell → nucleus
Scientists who study rock formations in caves describe some of the formations as “living rock” because, under certain conditions, they increase in size. Which statement would best dispute the claim that these rock formations are living?
(1) Rocks are not composed of cells, while living organisms are.
(2) Rocks perform complex metabolic processes, but cannot grow.
(3) Rocks cannot reproduce sexually.
(4) Rocks remain stable in a wide range of physical conditions.
Fish absorb oxygen through the gills, earth- worms absorb oxygen through the skin, amebas take in oxygen through the cell membranes, and cows inhale oxygen through the nasal passages into their lungs. This statement demonstrates that living things
(1) rely on similar or the same processes, but accomplish them in different ways
(2) rely on different processes and accomplish them in different ways
(3) rely on different processes, but perform them in the same or related ways
(4) have no relationship to one another, and are all independent individuals
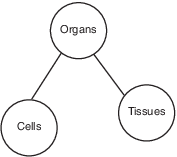
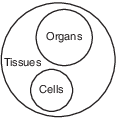
Which diagram best illustrates the relationship between the number of cells, tissues, and organs in a complex multicellular organism?
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 

Which statement correctly identifies the levels of organization for the structures indicated?
(1) A and B are tissues; E and G are organs.
(2) A and B are organs; E and G are systems.
(3) A and B are tissues; E and G are organelles.
(4) A and B are organelles; E and G are organs.
The diagram below represents the organization of structures within an organism.
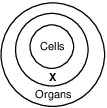
Which term best indicates the structures represented by the circle labeled X?
(1) organelles
(2) chromosomes
(3) organ systems
(4) tissues
Some levels of organization in a multicellular organism are shown in the sequence below.
A → cells → tissues → B → organ systems → organism
Which terms represented by letters A and B would complete the sequence?
(1) A–gametes; B–zygote
(2) A–zygote; B–gametes
(3) A–organs; B–organelles
(4) A–organelles; B–organs
The diagram below represents two organisms.

Which statement concerning organism A and organism B is correct?
(1) Organism A contains organs, whereas organism B lacks organs.
(2) Organism A and organism B have the same organ systems.
(3) Organism A and organism B both have structures that perform life processes.
(4) Organism A lacks structures that help maintain dynamic equilibrium.
The sequence below represents different organizational levels within the human body, from the simplest to more complex. Complete the sequence by correctly filling in the missing levels. [1]
organelles → ________________ → tissues → ________________ → organ systems → organism
Allow 1 credit for completing the diagram as shown below.
• organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems → organism
